Other
Johnson County Community College: Cell Membrane and Transport Mechanisms
Brief overview of the transport mechanisms involved in cell transport.
Kenyon College
Kenyon College: Passive Transport Versus Active Transport
A brief but clear explanation of passive and active transport. Examples are provided to further enhance clarity of the concepts.
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Diffusion: Lesson 2
This lesson explains the process of diffusion. It explains how diffusion is a passive form of transport, used to move molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 2 of 8 in the series titled "Diffusion."
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Diffusion: Lesson 4
This lesson explains the process of diffusion. It explains how diffusion is a passive form of transport, used to move molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 4 of 8 in the series titled "Diffusion."
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Facilitated Diffusion: Lesson 3
This lesson explains the process of facilitated diffusion, explaining that it is a passive form of transport which uses protein channels to move larger molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 3 of 9 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Facilitated Diffusion: Lesson 4
This lesson explains the process of facilitated diffusion, explaining that it is a passive form of transport which uses protein channels to move larger molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 4 of 9 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Facilitated Diffusion: Lesson 5
This lesson explains the process of facilitated diffusion, explaining that it is a passive form of transport which uses protein channels to move larger molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 5 of 9 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Facilitated Diffusion: Lesson 1
This lesson explains the process of facilitated diffusion, explaining that it is a passive form of transport which uses protein channels to move larger molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 1 of 9 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Osmosis: Lesson 2
This lesson explains the process of osmosis. It explains how osmosis is a passive form of transport, used to move water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, down their concentration gradient. It is 2 of 8 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Osmosis: Lesson 4
This lesson explains the process of osmosis. It explains how osmosis is a passive form of transport, used to move water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, down their concentration gradient. It is 4 of 8 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Osmosis: Lesson 1
This lesson explains the process of osmosis. It explains how osmosis is a passive form of transport, used to move water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, down their concentration gradient. It is 1 of 8 in the series titled...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Passive Transport: Lesson 3
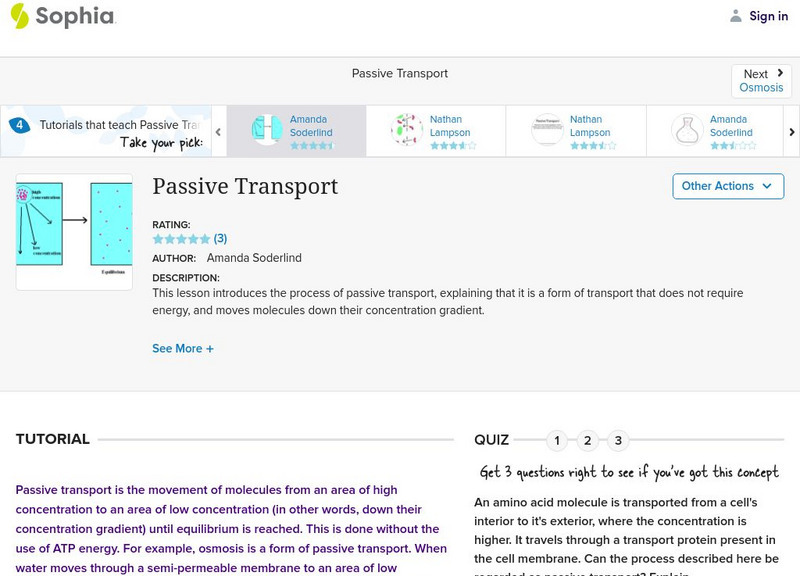
This lesson introduces the process of passive transport, explaining that it is a form of transport that does not require energy, and moves molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 3 of 4 in the series titled "Passive Transport."
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Passive Transport: Lesson 4
This lesson introduces the process of passive transport, explaining that it is a form of transport that does not require energy, and moves molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 4 of 4 in the series titled "Passive Transport."
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Passive Transport: Lesson 1
This lesson introduces the process of passive transport, explaining that it is a form of transport that does not require energy, and moves molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 1 of 4 in the series titled "Passive Transport."
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Diffusion: Lesson 1
This lesson explains the process of diffusion. It explains how diffusion is a passive form of transport, used to move molecules down their concentration gradient. It is 1 of 8 in the series titled "Diffusion."
Curated OER
Passive Transport in and Out of Cells
Diagram showing how passive transport works across a cell membrane.