TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: An Inflated Impression of Mars
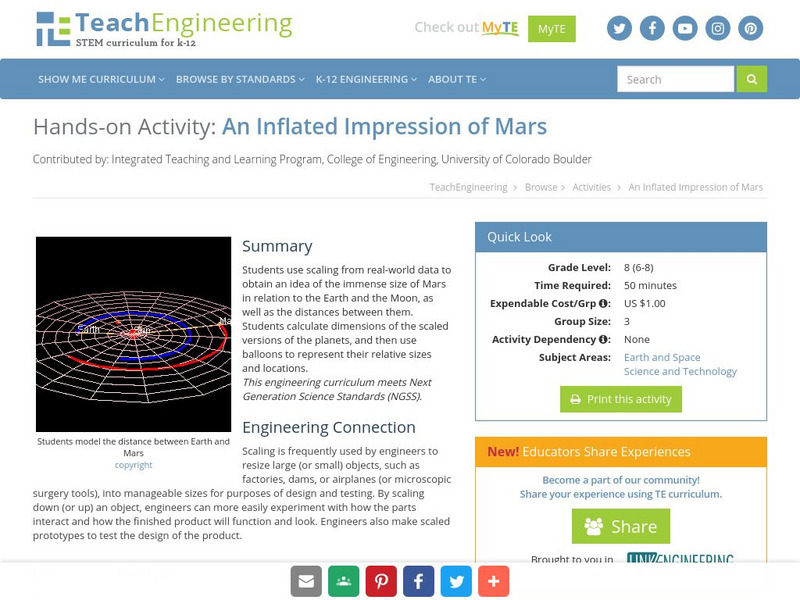
The purpose of this activity is to use scaling in order to give students an idea of the size of Mars in relation to the Earth and the Moon as well as the distance between them. The students will have to calculate dimensions of the scaled...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Strong Arm Tactics
Students generally do not know the complexity that goes into building and programming a robotic arm. In actuality, creating such an arm comes from a design that involves mechanical, electrical, and computer science engineers. This...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Edible Rovers
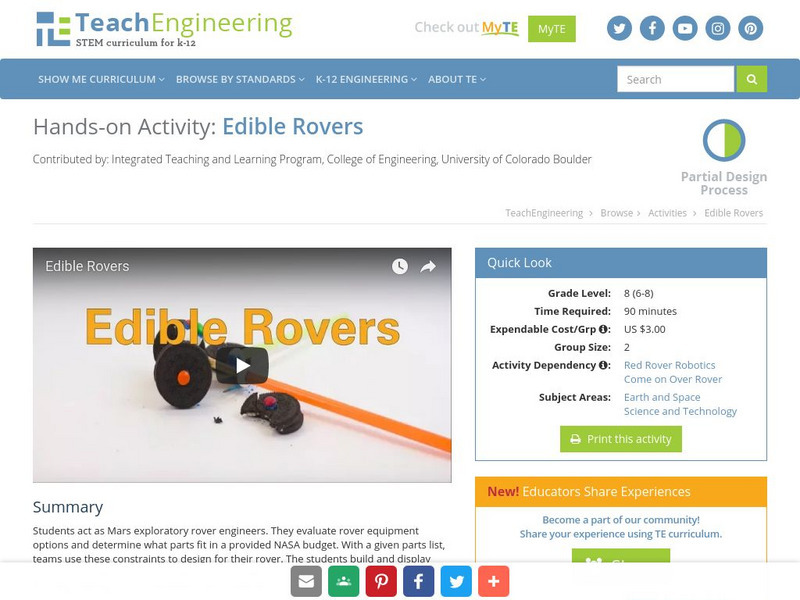
Students act as Mars exploratory rover engineers. They evaluate rover equipment options and determine what parts fit in a provided NASA budget. With a given parts list, teams use these constraints to design for their rover. The students...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Are We Alone?
The year is 2032 and your class has successfully achieved a manned mission to Mars! After several explorations of the Red Planet, one question is still being debated: "Is there life on Mars?" The class is challenged with the task of...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: In and Out Reactor
Students learn about material balances, a fundamental concept of chemical engineering. They use stoichiometry to predict the mass of carbon dioxide that escapes after reacting measured quantities of sodium bicarbonate with dilute acetic...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Give an Inch, Take a Foot
Students practice measuring techniques by measuring different objects and distances around the classroom. They practice using different scales of measurement in metric units and estimation. Also, students learn how measurement is used in...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Mint Mobiles
Students design, build and test model race cars made from simple materials (lifesaver-shaped candies, plastic drinking straws, Popsicle sticks, index cards, tape) as a way to explore independent, dependent and control variables. They...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Riding the Gravity Wave
Students write a biographical sketch of an artist or athlete who lives on the edge, riding the gravity wave, to better understand how these artists and athletes work with gravity and manage risk. Note: The literacy activities for the...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: The Big Mo
Momentum is not only a physical principle; it is a psychological phenomenon. Students learn how the "Big Mo" of the bandwagon effect contributes to the development of fads and manias, and how modern technology and mass media accelerate...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Action Reaction! Rocket
Students construct a rocket from a balloon propelled along a guide string. They use this model to learn about Newton's three laws of motion, examining the effect of different forces on the motion of the rocket.
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Couch Potato or Inertia Victim?
Students design a simple behavioral survey, and learn basic protocol for primary research, survey design and report writing. Note: The literacy activities for the Mechanics unit are based on physical themes that have broad application to...
TeachEngineering
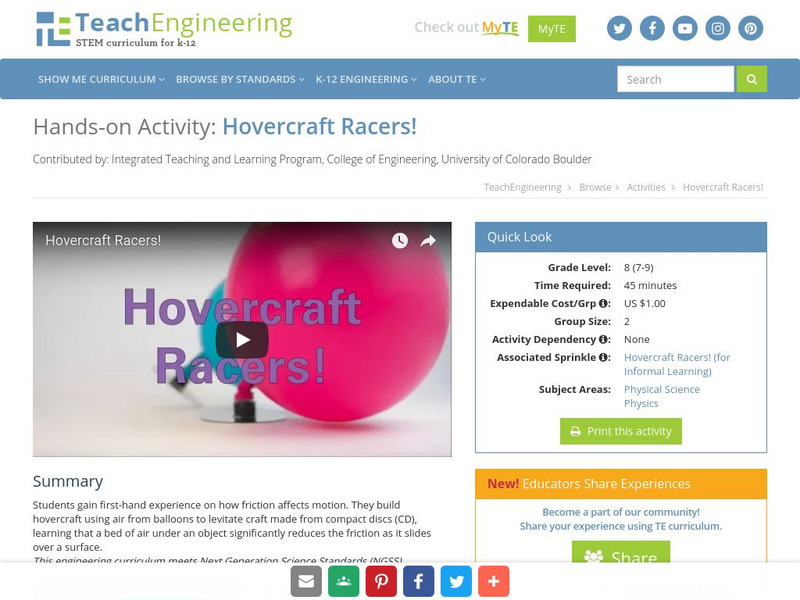
Teach Engineering: Hovercraft Racers!
Students gain first-hand experience on how friction affects motion. They build a hovercraft using air from a balloon to levitate a craft made from a compact disk (CD), learning that a bed of air under an object significantly reduces the...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: It Takes Two to Tangle
Students explore the theme of conflict in literature. They learn the difference between internal and external conflict and various types of conflicts, including self against self, self against other, and self against nature or machine....
TeachEngineering
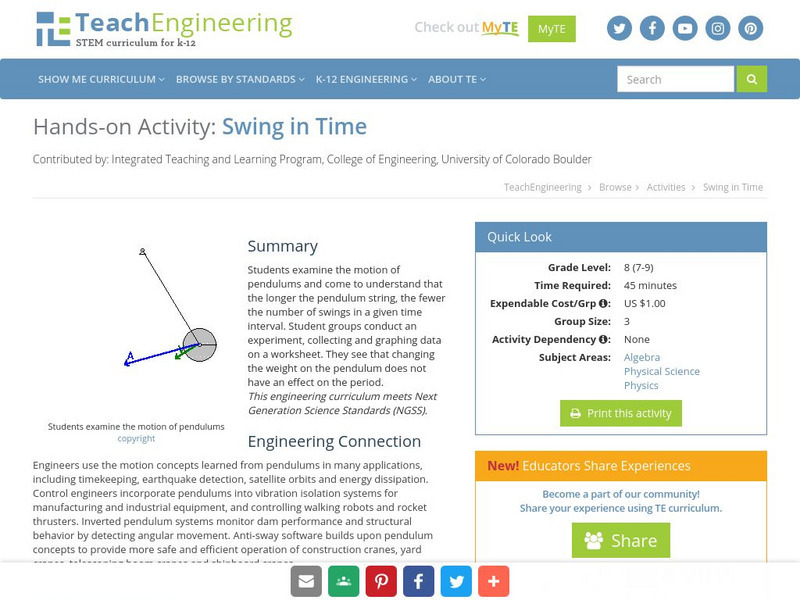
Teach Engineering: Swing in Time
Students examine the motion of pendulums and come to understand that the longer the string of the pendulum, the fewer the number of swings in a given time interval. They see that changing the weight on the pendulum does not have an...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Cars: Engineering for Efficiency
Students learn how the aerodynamics and rolling resistance of a car affect its energy efficiency through designing and constructing model cars out of simple materials. As the little cars are raced down a tilted track (powered by gravity)...
TeachEngineering
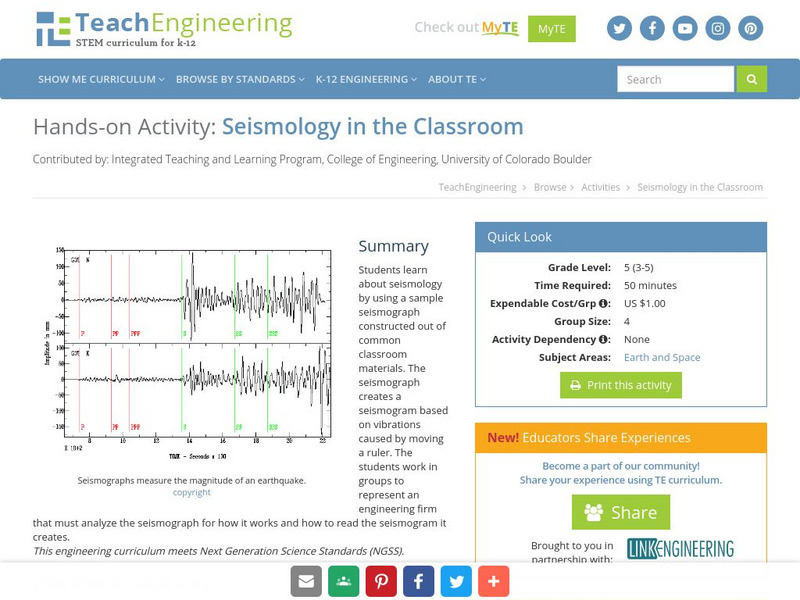
Teach Engineering: Seismology in the Classroom
Students learn about seismology by using a sample seismograph constructed out of common classroom materials. The seismograph creates a seismogram based on vibrations caused by moving a ruler. The students work in groups to represent an...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Ready to Erupt!
Students observe an in-classroom visual representation of a volcanic eruption. The water-powered volcano demonstration is made in advance, using sand, hoses and a waterballoon, representing the main components of all volcanoes. During...
TeachEngineering
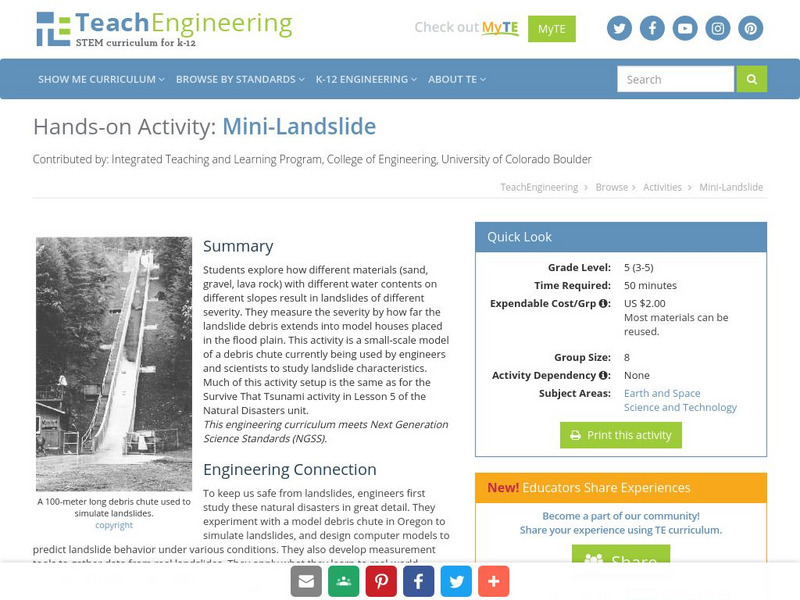
Teach Engineering: Mini Landslide
Students explore how different materials (sand, gravel, lava rock) with different water contents on different slopes result in landslides of different severity. They measure the severity by how far the landslide debris extends into model...
TeachEngineering
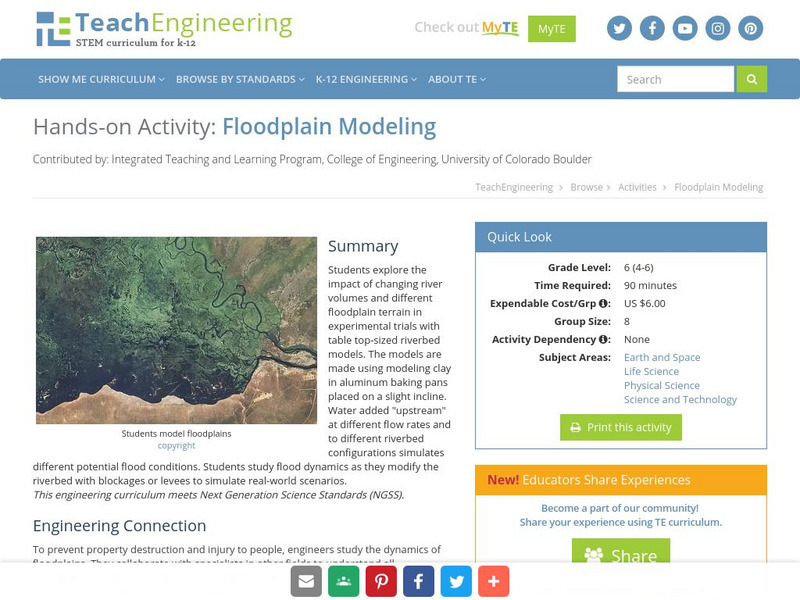
Teach Engineering: Floodplain Modeling
Students explore the impact of changing river volumes and different floodplain terrain in experimental trials with table top-sized riverbed models. The models are made using modeling clay in aluminum baking pans placed on a slight...
TeachEngineering
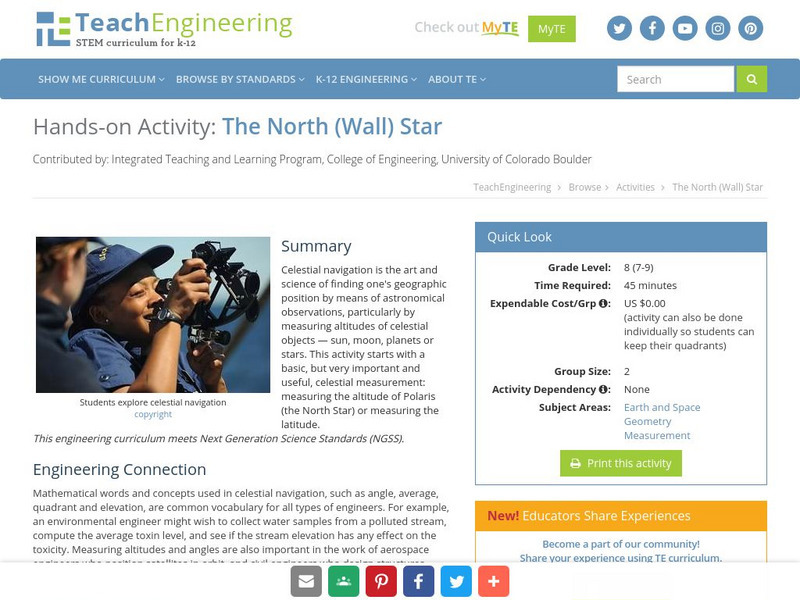
Teach Engineering: The North (Wall) Star
Celestial navigation is the art and science of finding one's geographic position by means of astronomical observations, particularly by measuring altitudes of celestial objects - sun, moon, planets or stars. This activity starts with a...
TeachEngineering
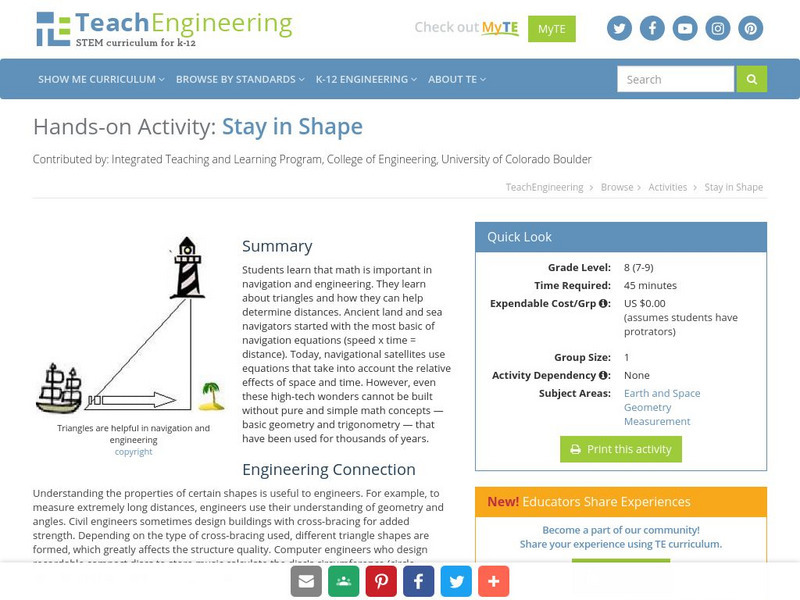
Teach Engineering: Stay in Shape
In this activity, students will learn that math is important in navigation and engineering. Ancient land and sea navigators started with the most basic of navigation equations (Speed x Time = Distance). Today, navigational satellites use...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Trig River
Students learn about and use a right triangle to determine the width of a "pretend" river. Working in teams, they estimate of the width of the river, measure it and compare their results with classmates.
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Close Enough?
Accuracy of measurement in navigation depends very much on the situation. If a sailor's target is an island 200 km wide, sailing off center by 10 or 20 km is not a major problem. But, if the island were only 1 km wide, it would be missed...
TeachEngineering
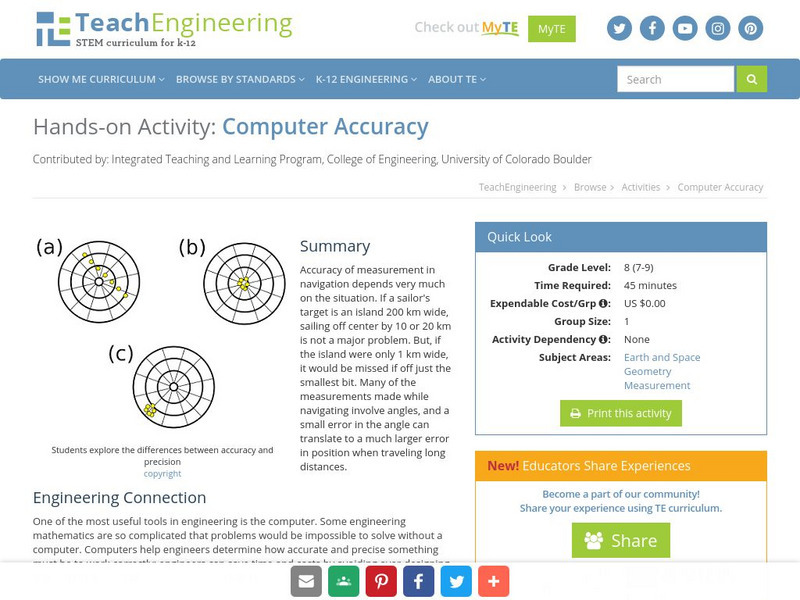
Teach Engineering: Computer Accuracy
Accuracy of measurement in navigation depends very much on the situation. If a sailor's target is an island 200 km wide, sailing off center by 10 or 20 km is not a major problem. But, if the island were only 1 km wide, it would be missed...