Vision Learning
Visionlearning: Earth Science: Rocks and Minerals: Defining Minerals
Instructional module focusing on minerals. Discussion includes chemical composition, chemical structure, and the formation process. The site also includes an interactive practice quiz and links relating to the topic.
TeachEngineering
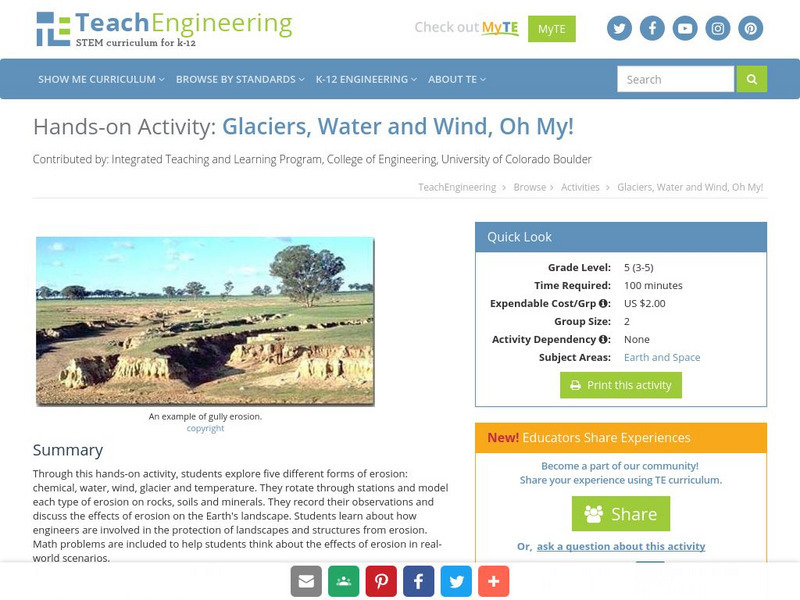
Teach Engineering: Glaciers, Water and Wind, Oh My!
This hands-on activity explores five different forms of erosion (chemical, water, wind, glacier and temperature). Students rotate through stations and model each type of erosion on rocks, soils and minerals. The students record their...
Science Struck
Science Struck: Salt Crystallization
Learn how salt crystallizes and the weathering effect that this has on rocks and on structures.
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: The Earth Is a Changin'
This lesson introduces and describes the main types of erosion (i.e., chemical, water, wind, glacier and temperature). Students learn examples of each type of erosion and discuss how erosion changes the surface of the Earth. Students...
Australian Museum
Australian Museum: Sedimentary Processes
Everything you need to know about sedimentary rocks and the processes by which they are created, including weathering, soils, environments, and classification.
Georgia Department of Education
Ga Virtual Learning: Landscape Evolution
In this amazing online tutorial you will learn about how water, mass wasting, weathering, and erosion have help shape the landforms on Earth. The lesson includes many helpful interactive materials to prepare help you understand landscape...
American Geosciences Institute
American Geosciences Institute: Earth Science Week: Rock Pop
Students investigate the process of rock being eaten away by acid, thus releasing carbon dioxide into the air.
Science Buddies
Science Buddies: Ozone Depletion
The ozone layer is important for blocking most of the harmful radiation that comes from the sun. You can find maps of the ozone layer and compare different regions of the globe for ozone coverage. Some scientists think that aerosols in...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Air Pollution
Students are introduced to the concept of air quality by investigating the composition, properties, atmospheric layers and everyday importance of air. They explore the sources and effects of visible and invisible air pollution. By...
Libre Text
Libre Texts: Geochemistry: The Earth and Its Lithosphere
The Earth has been in a state of continual change since its formation. The major part of this change, involving volcanism and tectonics, has been driven by heat produced from the decay of radioactive elements within the Earth. The other...
Math Science Nucleus
I. Science Ma Te: Integrating Science, Math and Technology
This site offers a wealth of online textbook-related materials that encourage the discovery of science in the world around us. Enter the site to access material on specific topics. Each section contains reading material (complete with...
University of Hawai'i
Pretty Green Mineral Pretty Dry Mars
Olivine-bearing rocks, similar to those found in Hawaii, have been found on Mars. Use this site to learn more about what has been found on Mars.
Other
Environment Canada: What Is Acid Rain?
A thorough explanation of acid rain with a focus on the following topics: what is acid rain, the pH scale measures acidity, what does acid rain do, and what can I do about acid rain.
Science Struck
Science Struck: Sedimentary Rock Formation Explained
Explains what sedimentary rocks are, the three main types, and how they are formed.
Michigan Reach Out
Reach Out Michigan: Acid Rain
This experiment from Reach Out Michigan "demonstrates the effect of acid rain on statues and buildings."
Climate Literacy
Clean: Introduction to Earth's Climate
This instructional activity is an introduction to Earth's climate and covers key principles regarding Earth's unique climate, atmosphere, and regional and temporal climate differences. Students will gain an understanding of how the...
Other
Abiotic Factors
Abiotic components are the nonliving components of the biosphere. Chemical and geological factors, such as rocks and minerals, and physical factors, such as temperature and weather, are referred to as abiotic components.