Colorado State University
If Hot Air Rises, Why Is it Cold in the Mountains?
Investigate the relationship between temperature and pressure. Learners change the pressure of a sample of air and monitor its temperature. They learn that as air decreases its pressure, its thermal energy converts to kinetic energy.
Colorado State University
Why Do Clouds Form in the Afternoon?
The stability of the atmosphere changes on a daily basis. A kinesthetic lesson models how the stability of the air changes as it's warmed by the sun. Learners connect their models to the changing air currents and movement of warm and...
Colorado State University
Do Cities Affect the Weather? (Making a Cloud in a Bottle)
The dynamics of a city can have a drastic effect on the weather. A hands-on lesson asks learners to build a model to illustrate how city pollution provides a nucleus for condensation. The greater the pollution, the greater chance for...
Curated OER
Worksheet 12: Functions
In this math worksheet, students are given 7 problems in which they differentiate, figure rate of change, determine value, and prove formulas.
Curated OER
The Laws of Thermodynamics
Pupils investigate the concept of a thermodynamic system. The difference between a state and phase is defined as part of the experimental explanations given in writing. Students conduct experiments to demonstrate laws of science like...
Alabama Learning Exchange
Researching Hurricanes with Technology
Students explain the components that make up a hurricane.
Curated OER
Rain Shadows and Sea Breezes
Students plot the average rainfall for a variety of cities in the United States. Using the map, they work together to determine patterns on which toxicants are transported through the air. They determine the impacts of various weather...
Curated OER
Heat Unit
Students define thermal equilibrium. They distinguish between internal energy and heat. Students describe how the quantity of heat that enters or leaves a substance is measured.
Physics Aviary
Physics Aviary: Practice Problems: Work Done in Adiabatic Compression Process
Determine the work that was done when no heat enters or leaves the system. A video describing the problem can be found here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vt0u94PtbJ8&feature=youtu.be
OpenStax
Open Stax: College Physics: The First Law of Thermodynamics
An online college physics textbook that explores the first law of thermodynamics by defining the processes of a simple heat engine. Section also describes the difference among isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, and adiabatic. Students will...
Texas Education Agency
Texas Gateway: The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes
By the end of this section, you will be able to describe the processes of a simple heat engine; explain the differences among the simple thermodynamic processes: isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, and adiabatic; and calculate total work...
Educaplus (Jesús Peñas Cano)
Educaplus: Transformaciones Termodinamicas [In Spanish]
Observe the difference between the isobars, isotherms, adiabatic, and isocore transformations.
Georgia State University
Georgia State University: Hyper Physics: Heat and Thermodynamics
Georgia State University Physics Department privides an incredibly thorough treatment of the laws of thermodynamics. Multiple pages; many informative graphics; opportunities to practice problems and receive immediate feedback.
University of Oregon
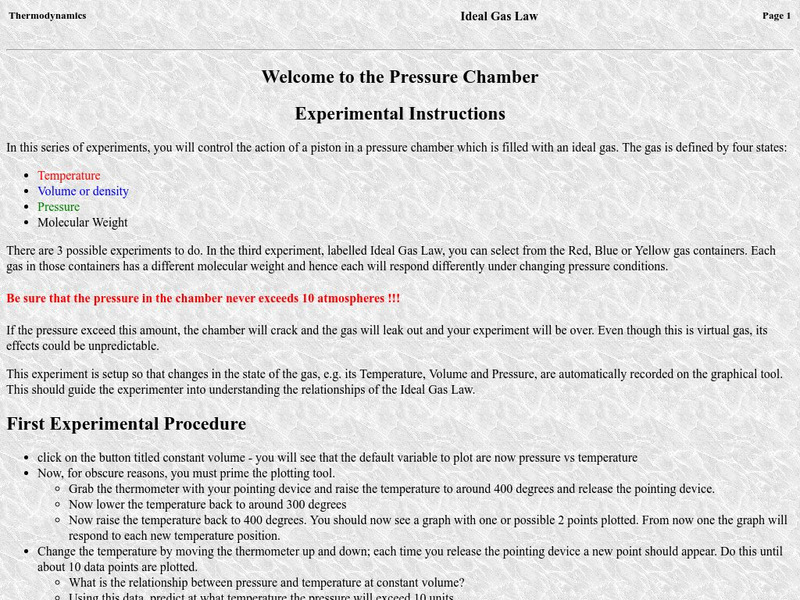
Welcome to the Pressure Chamber
This site has an online experiment for testing the ideal gas law.
Wikimedia
Wikipedia: Carnot Heat Engine
Wikipedia offers information on the Carnot heat engine that uses a particular thermodynamic cycle developed by Nicolas Carnot in 1820.
Georgia State University
Georgia State University: Hyper Physics: Heat Engine Concepts: The Otto Cycle
Schematic diagrams illustrating the operation of a four-stroke engine cycle. Interactive buttons allow you to step through the various steps of each engine cycle. Each graphic is accompanied by an excellent explanation.
Georgia State University
Georgia State University: Hyper Physics: Heat Engine Concepts: Carnot Cycle
The Carnot cycle is described, illustrated and explained. The Carnot efficiency equation is given and interactive JavaScript form allows the visitor to investigate the effect of the reservoir temperature and the sink temperature upon the...
Georgia State University
Georgia State University: Hyper Physics: Heat Engine Cycle
The heat engine cycle is defined and discussed. So pressure-volume diagrams are introduced and their use in depicting the cycles of a heat engine is demonstrated. Informative graphics are accompanied by reason-filled explanations.
Georgia State University
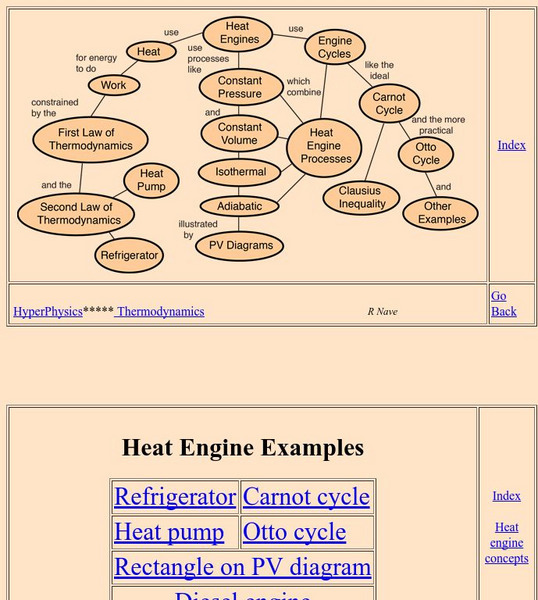
Georgia State University: Hyper Physics: Heat Engine Concepts
An indexing page for the HyperPhysics site. The page contains a concept map of links to a variety of other pages which discuss concepts related to heat engines. All pages contain informative graphics and excellent explanations.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Low Temperature Physics
Why do physicists want to study things at temperatures so cold atomic motion almost comes to a halt? And how do they create such frigid environments, anyway? Read on for the what, how and why of low temperature physics.
University of Sydney (Australia)
Thermal Physics Module: Refrigerators and Heat Pumps [Pdf]
Refrigerators and heat pumps are described. Their operation is explained and the variables which improve their efficiency is discussed.
University of Sydney (Australia)
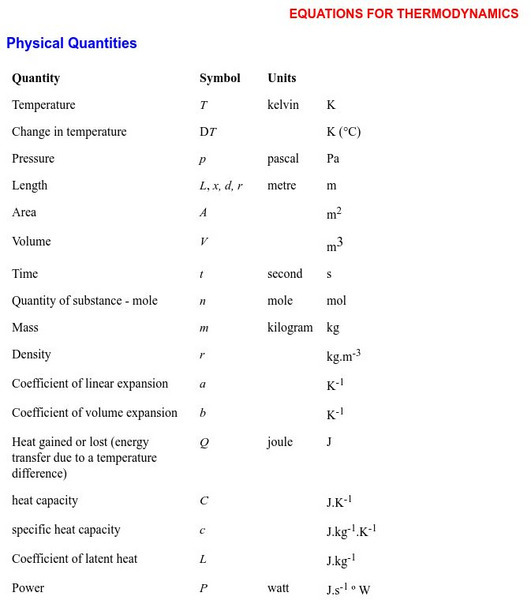
Equations for Thermodynamics
An exhaustive list of equations and formulas which are commonly used in thermal physics (including equations for triple point). Equations are organized according to category. Meaning of the symbols is clearly stated.













![Educaplus: Transformaciones Termodinamicas [In Spanish] Activity Educaplus: Transformaciones Termodinamicas [In Spanish] Activity](https://content.lessonplanet.com/knovation/original/366823-971322fb111d96f255f8c660d203ed63.jpg?1661772971)