Curated OER
Comparing and Ordering Integers
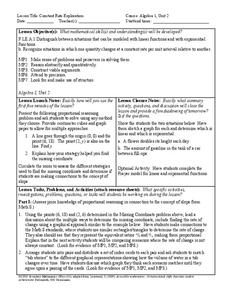
Young scholars compare and order integers on an umber line. In this algebra lesson plan, students differentiate between positive and negative numbers. They plot point in the correct order on a number line.
Curated OER
Introduction To Data Analysis
Seventh graders investigate the concept of looking at the data put in a variety of ways that could include graphs or data sets. They analyze data critically in order to formulate some sound conclusions based on real data. Students graph...
Curated OER
Exponential Functions: Half Life and Doubling Time
Students investigate the concept of exponential functions and how they increase in size over time. They simplify the functions in order to find the solutions that are possible and perform analysis of the curved line that is produced when...
Curated OER
Equations of Horizontal and Vertical Lines
Young scholars are given graphs of lines and asked to write an equation. In this algebra lesson, students are asked to write the equations for horizontal and vertical lines. They write equations for line crossing and going through...
Curated OER
The Bigger they Are . . .
Students do a variety of data analyses of real-life basketball statistics from the NBA. They chart and graph rebounding, scoring, shot blocking and steals data which are gathered from the newspaper sports section.
EngageNY
Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
Arithmetic and geometric sequences are linear and geometric patterns. Help pupils understand the relationship and see the connection with an activity that asks them to write the rules and classify the patterns correctly. A sorting...
Curated OER
Linear Progression
Students use graphing calculators to graph lines and create tables of values. They perform an experiment using M&M's and slinkys, then create their tables based on their results.
Curated OER
"Ball Bounce" Quadratic Functions
Young scholars manipulate a ball and explore quadratic functions. In this algebra lesson, learners analyze the graph of a quadratic function. They identify quadratic properties.
Curated OER
Lines, Rays, Line Segments, and Planes
Students are introduced to lines, rays, line segments and planes and study the differences between them. They also practice graphing lines, rays, line segments and planes
EngageNY
Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
Many learners find completing the square the preferred approach to solving quadratic equations. Class members combine their skills of using square roots to solve quadratics and completing the square. The resource incorporates a...
Curated OER
Slope Fields
Students sketch a slope field for a given differential equation, given a slope field. They also match a slope field to a differential equation and match a slope field to a solution of a differential equation. Finally, students use a...
Curated OER
Equations of Conics
Students investigate the graphs of conics. In this Algebra II lesson, students solve equations of conics while playing the game of Tracker. In Tracker the graphs are hidden on a coordinate plane and students use probe shots...
Curated OER
The Sum of Our Integer Intelligences
Students complete tasks. In this Seven Intelligences instructional activity, students complete a variety of activities that are all based on the seven different intelligences humans are supposed to possess based on Dr. Gardener's theory....
Curated OER
Integration: Statistics, Scatter Plots and Best-Fit Lines
In this math worksheet, students identify the type (if any) of correlation on 6 scatter plots. They use information given on a table to create a scatter plot and identify the type of correlation. Students use the scatter plot to make...
Curated OER
Properties of Logarithms
Students explore the concept of logarithms. In this logarithms lesson plan, students discuss the logarithm properties. Students use linear functions as a basis to develop the logarithm properites by substituting log b and log...
Howard County Schools
Constant Rate Exploration
Question: What do rectangles and bathtub volume have in common? Answer: Linear equations. Learn how to identify situations that have constant rates by examining two different situations, one proportional and one not proportional.
Georgia Department of Education
Math Class
Young analysts use real (provided) data from a class's test scores to practice using statistical tools. Not only do learners calculate measures of center and spread (including mean, median, deviation, and IQ range), but...
Virginia Department of Education
The Exercise Fields
Horses need exercise, too. Scholars create linear equations to model the perimeter of exercise fields for horses. They finish by solving their equations for the length and width of the fields.
Curated OER
Interesting Properties of Cubic Functions to Discover Graphically or Numerically
Learners investigate the slope of a cubic function. They find the tangent line of the cubic function at point P, and discuss the relationship between point P and point Q, the point the tangent line intersects the cubic function. ...
Curated OER
Approximation of Pi
Learners explore the concept of Pi. In this Pi lesson, students measure the circumference and diameter of a circle. Learners record the diameter and circumference measurements from their classmates. Students enter the...
Curated OER
Chronic Conics
Fourth graders use two activities to draw four different conic sections. One activity is of a physical nature and one is traditional paper and pencil.
Curated OER
The Mandelbrot Set
Students are introduced to the notion of a complex number and function iteration in order to motivate the discussion of Julia sets and the Mandelbrot set.
Curated OER
Carshop!
Learners explore the concept of interest. In this interest lesson, students shop for cars and determine the payments and interest rates for various cars. Learners use various websites to research cars and interest rates for car loans....
Curated OER
Make Your Own "Weather" Map
Students develop and apply a variety of strategies to solve problems, with an emphasis on multi-step and non-routine problems. They acquire confidence in using mathematics meaningfully.