Khan Academy
Khan Academy: A Compound in Equality With No Solution
Sal solves the compound inequality 5x-3<12 AND 4x+1>25, only to realize there's no x-value that makes both inequalities true.
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Applications of Compound Inequalities
Here we look at how to relate compound inequalities to real world problems.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Formula for Continuously Compounding Interest
Learn how to calculate interest when interest is compounded continuously. This video compares the effects of compounding more than annually, building up to interest compounding continually. [8:58]
Virtual Nerd
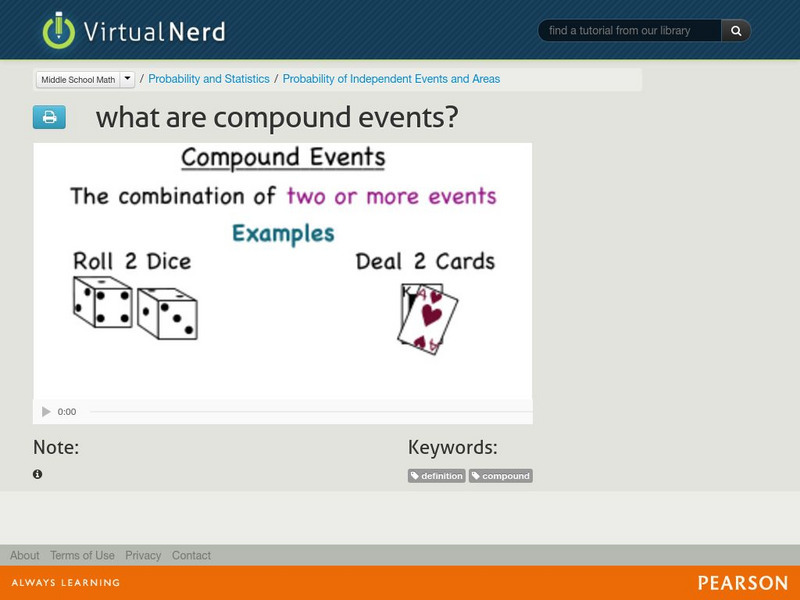
Virtual Nerd: What Are Compound Events?
What if we want to find the probability of more than one event occurring? This would be a compound event. Watch this video for an explanation and example. [3:29]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2
A video about absolute value inequalities.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Diastereomers and Meso Compounds: Stereoisomers, Enantiomers,
This video looks at pairs of molecules to see if they relate to each other in obvious or less than obvious ways, for example, by having the same molecular formula but different structures. The video looks at stereoisomers, enantiomers,...
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Absolute Value Inequalities Example 3
A video about absolute value inequalities.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Simple and Compound Sentences
A simple sentence contains one independent clause. A compound sentence contains more than one! Put another way: a simple sentence contains a subject and a predicate, but a compound sentence contains more than one subject and more than...
Sophia Learning
Sophia: Solving Multi Step Linear Inequalities #3
This lesson presents how to solve linear inequalities that involve more than one operation.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Writing and Using Inequalities
Compound and absolute value inequalities: writing and using inequalities.
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Interest (Part 2)
Expand the equation to calculate simple interest for a single period, P*(1+r), to calculate interest when interest is charged for more than one period and that interest is compounded at different intervals. [8:02]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Common and Systematic Naming Prefixes
There is a logical system in which to name carbon chains as described here. The naming system becomes more logical when there are more than five compounds in the chain. Understand the prefixes: iso-, sec- and tert-. [13:29]
Khan Academy
Khan Academy: Algebra: Algebra Ii: Functions, Combinatorics
Video solving problems 60 to 65 of the California Standards Test for Algebra II. Concepts covered include negative exponents, square root equations and inequalities, permutations, and probability. [11:25]
Tyler DeWitt, PhD
Tyler De Witt: Writing Empirical Formula Practice
In this video you will practice writing empirical formulas for many molecular formulas. In order to write the empirical formula, you find the largest number you can divide all of the subscripts by, to reduce it as much as possible. You...