National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Sin Itiro Tomonaga
Japanese theoretical physicist Sin-Itiro Tomonaga resolved key problems with the theory of quantum electrodynamics (QED) developed by Paul Dirac in the late 1920s through the use of a mathematical technique he referred to as...
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Jean Charles Athanase Peltier (1785 1845)
Although he didn't start studying physics until he retired from the clock-making business at age 30, French native Jean Peltier made immense contributions to science that still reverberate today. Even with the primitive tools available...
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Charles Augustin De Coulomb
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb invented a device, dubbed the torsion balance, that allowed him to measure very small charges and experimentally estimate the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies. The data he obtained...
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Crookes Tube 1870
English chemist Sir William Crookes (1832 - 1919) invented the Crookes tube to study gases, which fascinated him. His work also paved the way for the revolutionary discovery of the electron and the invention of X-ray machines.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Transatlantic Telegraph Cable 1858
The main figure behind the first transatlantic telegraph knew very little about the science or engineering behind it, but was convinced that with it a fortune could be made. Read about these findings here.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Steam Condensing Engine 1769
Few inventions have affected human history as much as the steam engine. Without it, there would have been no locomotives, no steamers and no Industrial Revolution.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Paul Dirac
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac was an outstanding twentieth century theoretical physicist whose work was fundamental to the development of quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics jointly with...
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: John Bardeen
John Bardeen was one of a handful of individuals awarded the Nobel Prize twice and the first scientist to win dual awards in physics. Both times, he shared the prize with others. The first time his co-recipients were Walter Brattain and...
Science Struck
Science Struck: The Relationship Between Magnetism and Electricity
Provides a short explanation of the similarities between magnetism and electricity, the properties of their fields, and the effect they each have on a charged particle.
Florida State University
Florida State University: Magnet Lab: Electric Meter 1872
The invention of the light bulb quickly created the need to track people's electricity usage. In 1872, Samuel Gardiner built the first simple power meter: a lamp with an attached clock that recorded the time the light was on.
Orpheus Books
Q Files: Electricity and Magnetism: Electric Charge
Learn how electric charges work and about Coulomb's Law, which is used to calculate the strength of an electric force.
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Heat Resistance
Heating a metal conductor makes it more difficult for electricity to flow through it. See why in this tutorial. (Java tutorial)
Sophia Learning
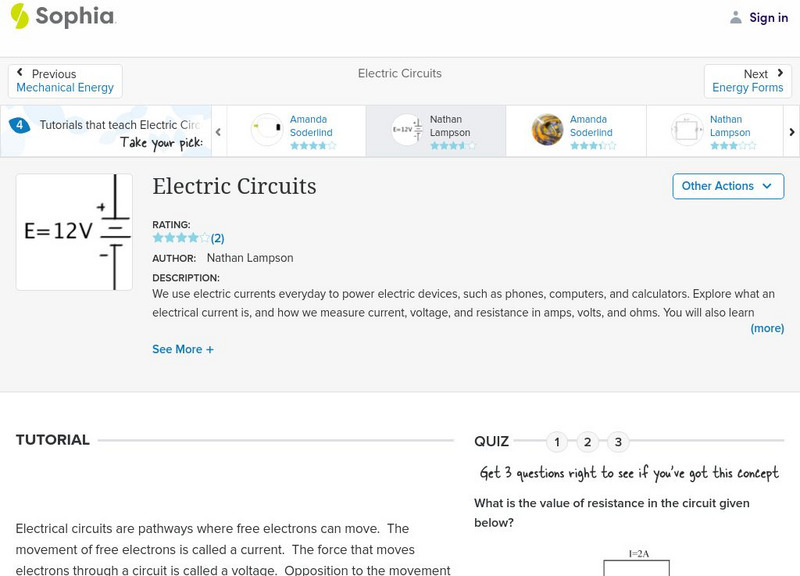
Sophia: Electric Circuits: Lesson 2
This lesson will explain how to calculate voltage, current, and resistance in simple electric circuits. It is 2 of 4 in the series titled "Electric Circuits."
Sophia Learning
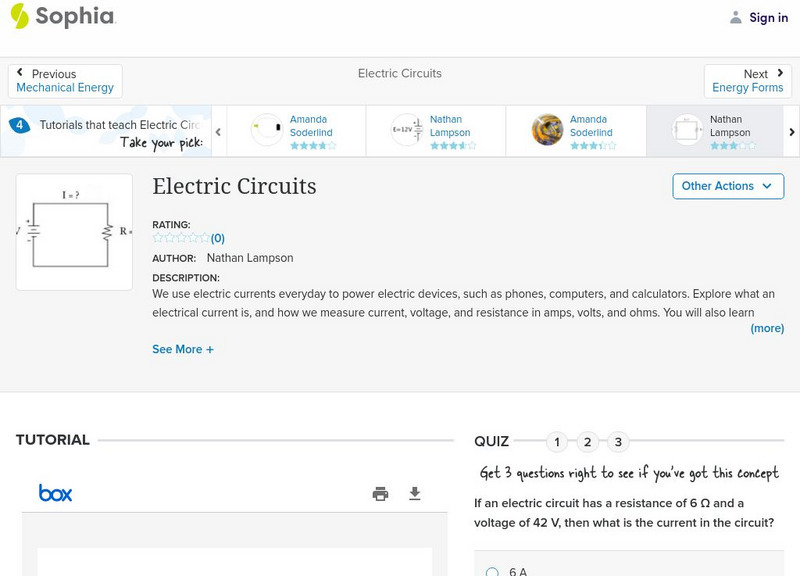
Sophia: Electric Circuits: Lesson 4
This lesson will explain how to calculate voltage, current, and resistance in simple electric circuits. It is 4 of 4 in the series titled "Electric Circuits."
Science4Fun
Science4 Fun: How Electricity Is Made
Read this brief article to gain an understanding of the principle of electromagnetism, how electricity is generated, and the problem with fossil fuels.
Other
Ithaca Hs Ny/electrical Generator Ac or Dc/applet
What a lovely little applet! You can speed/slow it, change it from AC to DC, plot the voltage as it rotates, change direction, control other information. Real neat.
Science Bob Pflugfelder
Science Bob: Build an Electromagnet!
This site presents a procedure for creating your own electromagnet using an iron nail, some wire, and a battery. The site illustrates a connection between electricity and magnetism.
Physics4kids
Physics4 Kids: Electricity and Magnetism: Current
Explains electric current, how it produces heat, and the difference between a direct current and an alternating current.
Ducksters
Ducksters: Practice Science Questions: Easy Electronics and Magnetism
Practice science questions on the subject of easy electronics and magnetism can be found on this website.
Ducksters
Ducksters: Practice Science Answers: Easy Electronics and Magnetism
Find the answers to the science quiz on the subject of easy electronics and magnetism on this site.
Read Works
Read Works: Electric and Magnetic Forces and the Modern Day Compass
[Free Registration/Login Required] An informational text about how a compass works using electromagnetic force. A question sheet is available to help students build skills in reading comprehension.
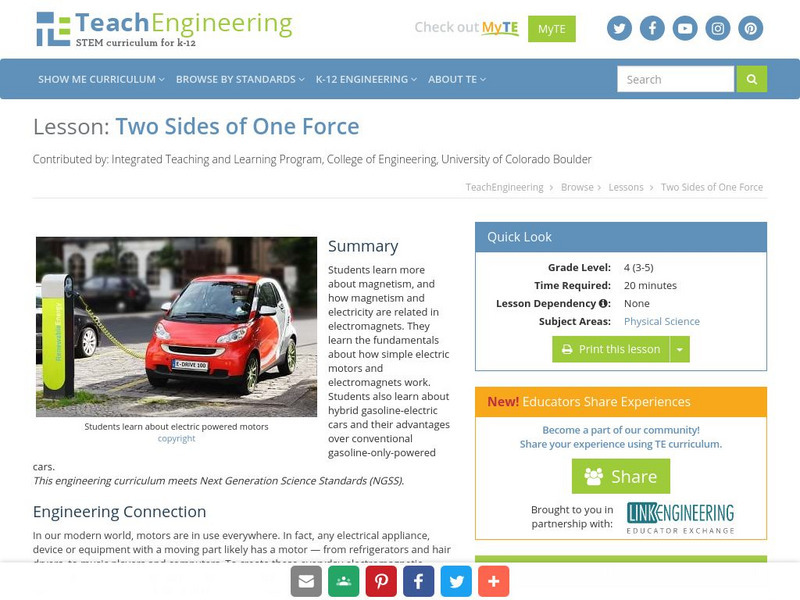
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Two Sides of One Force
Learners learn more about magnetism, and how magnetism and electricity are related in electromagnets. They learn the fundamentals about how simple electric motors and electromagnets work. Students also learn about hybrid...
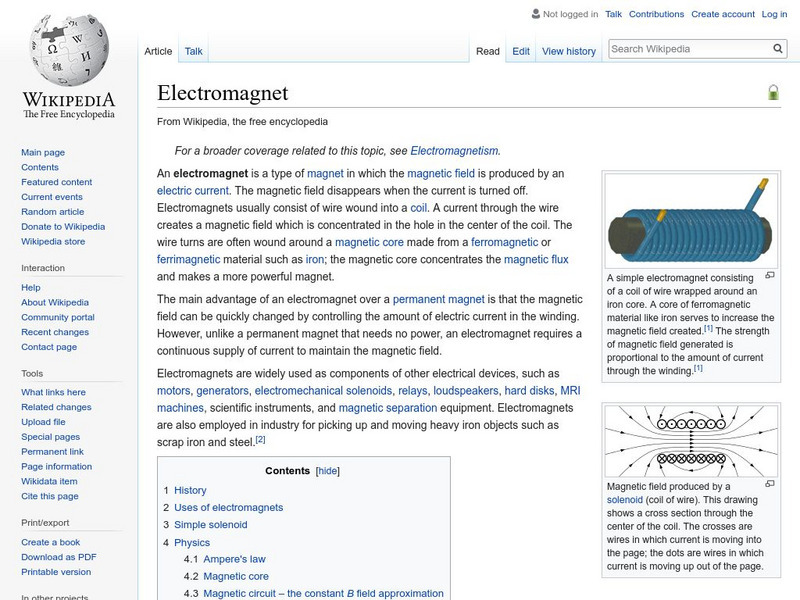
Wikimedia
Wikipedia: Electromagnet
Easy-to-read information and an illustration of an "electromagnet," a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is induced by the flow of an electric current.
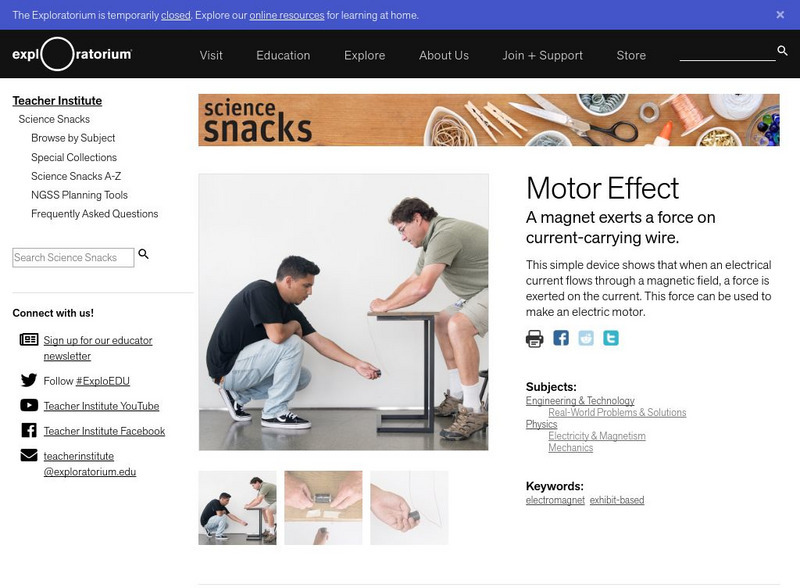
Exploratorium
Exploratorium: Science Snacks: Motor Effect
"A magnet exerts a force on current-carrying wire." This simple device shows how magnets affect wires with current in them, the basis of the electric motor. If you see, feel and understand this, the electric motor becomes very clear.