EngageNY
Building Logarithmic Tables
Thank goodness we have calculators to compute logarithms. Pupils use calculators to create logarithmic tables to estimate values and use these tables to discover patterns (properties). The second half of the lesson has scholars use given...
EngageNY
Transformations of the Quadratic Parent Function
Efficiently graph a quadratic function using transformations! Pupils graph quadratic equations by completing the square to determine the transformations. They locate the vertex and determine more points from a stretch or shrink and...
EngageNY
Characterize Points on a Perpendicular Bisector
Learn transformations through constructions! Pupils use perpendicular bisectors to understand the movement of a reflection and rotation. They discover that the perpendicular bisector(s) determine the line of reflection and the...
EngageNY
Representing, Naming, and Evaluating Functions (Part 1)
Begin the discussion of domain and range using something familiar. Before introducing numbers, the lesson uses words to explore the idea of input and outputs and addresses the concept of a function along with domain and range.
EngageNY
Linear Functions and Proportionality
Connect linear equations, proportionality, and constant rates of change to linear functions. Young mathematicians learn how linear equations of the form y = mx + b can represent linear functions. They then explore examples of linear...
EngageNY
Definition of Translation and Three Basic Properties
Uncover the properties of translations through this exploratory lesson. Learners apply vectors to describe and verify transformations in the second installment of a series of 18. It provides multiple opportunities to practice this...
EngageNY
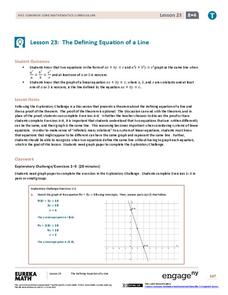
The Defining Equation of a Line
They appear to be different, yet they are the same line. Part 24 out of 33 lessons provides a theorem about the relationships of coefficients of equivalent linear equations. Pupils use the theorem to determine whether two equations are...
EngageNY
Representations of a Line
Explore how to graph lines from different pieces of information. Scholars learn to graph linear functions when given an equation, given two points that satisfy the function, and when given the initial value and rate of change. They solve...
EngageNY
Using Linear Models in a Data Context
Practice using linear models to answer a question of interest. The 12th installment of a 16-part module combines many of the skills from previous lessons. It has scholars draw scatter plots and trend lines, develop linear models, and...
Curated OER
When Will We Ever Use This? Predicting Using Graphs
Here are a set of graphing lessons that have a real-world business focus. Math skills include creating a scatter plot or line graph, fitting a line to a scatter plot, and making predictions. These lessons are aimed at an algebra 1...
EngageNY
Graphs of Piecewise Linear Functions
Everybody loves video day! Grab your class's attention with this well-designed and engaging resource about graphing. The video introduces a scenario that will be graphed with a piecewise function, then makes a connection to domain...
EngageNY
Prove the Pythagorean Theorem Using Similarity
Amaze your classes with the ability to find side lengths of triangles immediately — they'll all want to know your trick! Learners use the Pythagorean Theorem and special right triangle relationships to find missing side lengths.
EngageNY
Secant Lines; Secant Lines That Meet Inside a Circle
Young mathematicians identify different cases of intersecting secant lines. They then investigate the case where secant lines meet inside a circle.
EngageNY
Sampling Variability in the Sample Proportion (part 1)
Increase your sample and increase your accuracy! Scholars complete an activity that compares sample size to variability in results. Learners realize that the greater the sample size, the smaller the range in the distribution of sample...
EngageNY
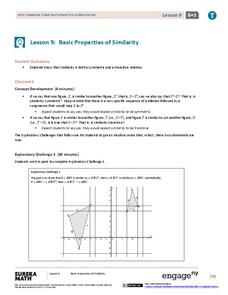
Basic Properties of Similarity
Does the symmetry and transitive property apply to similarity? The 10th segment in a series of 16 presents the class with a group of explorations. The explorations have pairs show that similarity is both symmetrical and transitive....
EngageNY
Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
Discover a new application of the Pythagorean Theorem. Learners prove and apply the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem in the 17th lesson in a 25-part series. The examples ask learners to verify right triangles using the converse...
National Gallery of Canada
A Cultural Portrait
Explore heritage and identity through an examination of art and a related project. The featured art, related to the African diaspora, includes several types of art created by different artists. Pupils consider their own backgrounds and...
EngageNY
Why Are Vectors Useful? 2
Investigate the application of vector transformations applied to linear systems. Individuals use vectors to transform a linear system translating the solution to the origin. They apply their understanding of vectors, matrices,...
EngageNY
Tangent Lines and the Tangent Function
Construct tangent lines and make the connection to tangent functions. An informative instructional activity reviews the geometry origins of the tangent function. Pupils use that information to determine how to construct a tangent to a...
Illustrative Mathematics
Games at Recess
A great non-calculation problem that lets your math minds explore without the pressure of the right answer. Your learners will have to compare boys and girls playing soccer and jump rope during recess. How many more boys than girls are...
Louisiana Department of Education
Essential Elements Cards
Use essential elements cards to help lesson plan! Each card contains an informational text common core standard for grade levels six through eight and suggestions for activities and supports. Cards address skills such as citing textual...
Illustrative Mathematics
Introduction to Linear Functions
Introduce your algebra learners to linear and quadratic functions. Learners compare the differences and relate them back to the equations and graphs. Lead your class to discussions on the properties of a function or a constant slope...
EngageNY
Grade 10 ELA Module 1: Unit 2, Lesson 1
The complex relationship between a teacher and his student takes center stage in an instructional activity that asks readers to pay close attention to how author Ethan Canin introduces his characters and how he develops the character of...
Curated OER
Creating a Pot: Repetition as a Unifying Design Element
Students use subjects, themes, and symbols that demonstrate knowledge of contexts, values, and aesthetics that communicate intended meaning in artworks.