Science Matters
Spaghetti Fault Model
Does increasing the pressure between two moving plates provide a stabilizing force or create more destruction? The hands-on lesson encourages exploration of strike-split fault models. The sixth lesson in a 20-part series asks...
Curated OER
A Model of Three Faults
Young scholars observe fault movements on model of the Earth's surface, find fault movements associated with different types of plate boundaries, research examples of non-plate boundary faults, and research and report on the types of...
Curated OER
Teaching About Plate Tectonics and Faulting Using Foam Models
Young scientists learn about plate tectonics and the three different types of faults (normal, reverse, and strike-slip) using foam models. The activity also covers common types of locations where these faults are found.
Science Matters
A Model of Plate Faults
The San Andreas fault is one of the longest fault zones in the world. In a series of 20 lessons, the fourth lesson has pupils use a paper model to recreate various types of plate faults. Each is held in position then drawn...
Science Matters
Up and Down Fault Blocks
The Sierra Mountains in Nevada and the Tetons in Wyoming originally formed as fault block mountains. In order to visualize these fault blocks, pupils use construction paper to create layers of earth. They cut the paper models and form...
Science Matters
Fault Formations
The San Andreas Fault moves about two inches a year, approximately the same rate fingernails grow—crazy! The third activity in the series allows for hands-on exploration of various fault formations. Through the use of a Popsicle stick,...
Curated OER
Stressed to a Fault!
Eighth graders describe how stress builds up in the Earth's crust by the movement of tectonic plates. In groups, they relate the three types of stresses to the types of plate movements and explain how the stress causes faults to form. ...
Curated OER
Moving the Earth
Fifth graders simulate the three primary types of fault movement lateral fault, reverse fault, and normal fault by positioning their hands and applying pressure to them to observe the similar action taking place in the Earth's crust.
Curated OER
Take a Stab!
Your geology class practices taking core samples of a potato to examine the stratigraphy. This is a terrific modeling lesson that helps youngsters visualize strata that cannot be seen from the surface of the ground. The directions...
Curated OER
A Model of Three Faults
Students investigate faults. In this science lesson, students explore the many stresses and strains in the earth's layers and research the types of faults in their state.
Curated OER
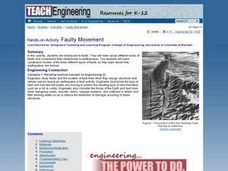
Faulty Movement
Students discover the faults throughout the Earth. They describe the different types of faults and how they are related to earthquakes. They build models of the faults.
Science Matters
Slip Sliding Along
The San Andreas Fault is the largest earthquake-producing fault in California. In the seventh instructional activity in the 20 part series, pupils create maps of California, focusing on the San Andreas Fault system. The comparison...
Curated OER
Puzzle of the Plates
Students research tectonic plates and their movement. In this plate lesson, students describe the motion of these plates and the boundaries between them. They look into the San Andreas Fault and explore the earthquakes associated to this...
Curated OER
Earthquake Formation
Students explore earthquakes. In this natural disaster and engineer career education lesson, students identify features of the earth's surface that increase the likelihood of an earthquake. Students use visual aids to locate the earth's...
Curated OER
Stick-Slip Movement
Ninth graders operate a model to observe the type of motion that occurs at a fault during an earthquake. They explore the effects of several variables. Students measure movement, calculate averages and plot and graph information.
Curated OER
Rock Layers
Students interpret a rock core sample from a clay model. In small groups, they layer modeling clay in a plastic container using coarse-grained spices sprinkled in to represent fossils. They switch containers with another group and remove...
Curated OER
Which Boundary Am I?
Sixth graders find 12 statements which describe the characteristics of the three boundary types, arranged in random order. Their task is to read each statement, and then CUT and PASTE it to the the appropriate boundary icon.
Curated OER
Candy Quakes
Eighth graders use candy to show the effects of deformation forces on the earth's crust. In this rock and fossil formation instructional activity students construct models and simulations to describe and explain natural phenomena.
Curated OER
Plate Tectonics
Students simulate the three types of plate boundaries using robots. For this earth science lesson, students explain how earthquakes and volcanoes are formed. They collect real-world earthquake data and plot them on the map.
Alabama Learning Exchange
Action at Plate Boundaries
Students diagram the spreading of the ocean floor. In this earth science lesson plan, students read an article on plate boundaries of the ocean. Students are expected to diagram the oceanic convergent boundary, and...
Curated OER
Earth's Plate Tectonics
Students identify the different layers of the Earth. In this earth science lesson, students create a model of the crusts and continents. They explain how plates movement cause earthquakes and volcanoes.
Curated OER
Slinky Lab- Simulating the Motion of Earthquake Waves
Sixth graders simulate primary and secondary waves. In this earthquakes waves lesson, 6th graders experiment using a slinky to gain understanding of how waves are created during an earthquake. Students record observations in drawings....
Curated OER
Geologic cross section of Manhattan, NYC
Students draw an accurate geologic cross section by using a given data table. They relate the features of the cross section to geologic processes. Students then relate the characteristics of the bedrock to the architecture.
Curated OER
Candy Quakes
Eighth graders, using a candy bar, gum, and Twizzlers, demonstrate the effects of deformational forces on the earth's crust. They examine the processes of rock and fossil formation.