TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Hovercraft Racers!
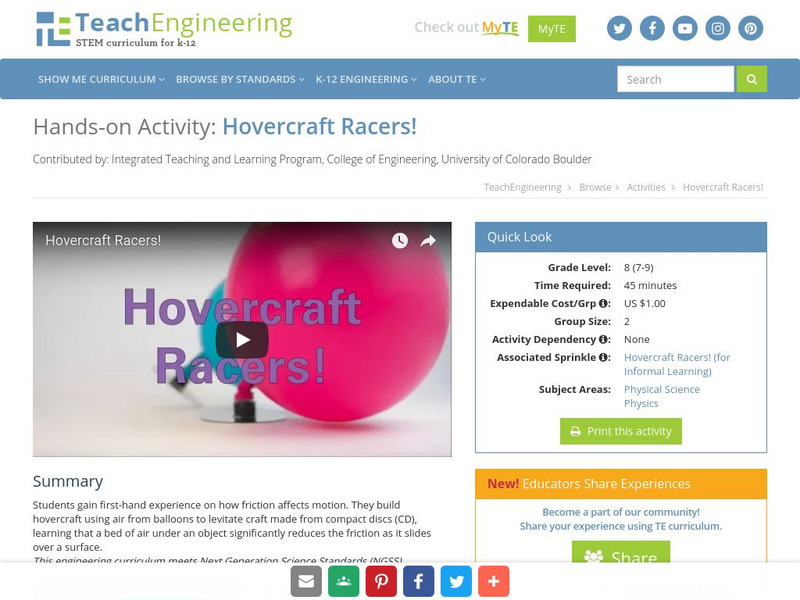
Students gain first-hand experience on how friction affects motion. They build a hovercraft using air from a balloon to levitate a craft made from a compact disk (CD), learning that a bed of air under an object significantly reduces the...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: It Takes Two to Tangle
Students explore the theme of conflict in literature. They learn the difference between internal and external conflict and various types of conflicts, including self against self, self against other, and self against nature or machine....
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Team Up!
Students explore the physical and psychological effect of stress and tension on human beings. They develop their observing, thinking, writing and teamwork skills by working on a group art project and reporting about it. They learn about...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Swing in Time
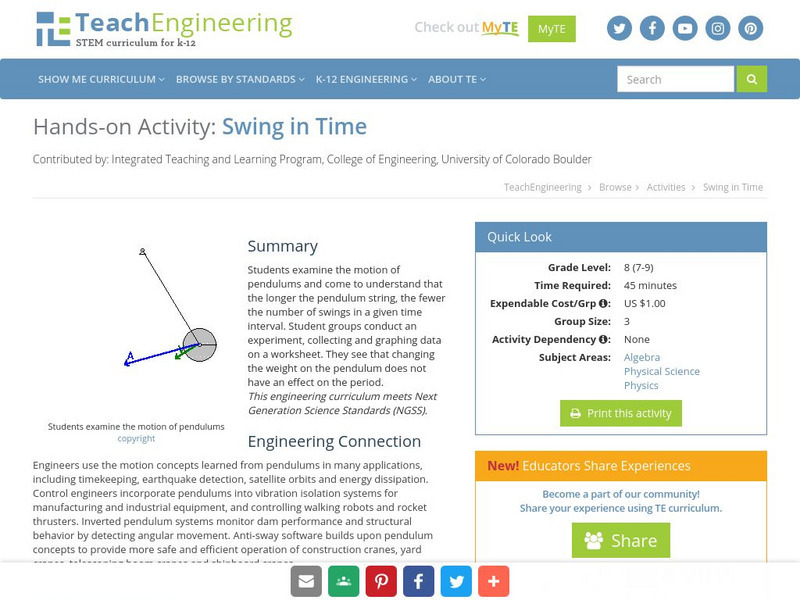
Students examine the motion of pendulums and come to understand that the longer the string of the pendulum, the fewer the number of swings in a given time interval. They see that changing the weight on the pendulum does not have an...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Stress, Inc.
Students explore the physical and psychological effect of stress and tension on human beings. Concepts of stress and stress management are introduced. Students discover how perception serves to fuel a huge industry dedicated to...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Cars: Engineering for Efficiency
Students learn how the aerodynamics and rolling resistance of a car affect its energy efficiency through designing and constructing model cars out of simple materials. As the little cars are raced down a tilted track (powered by gravity)...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Seismology in the Classroom
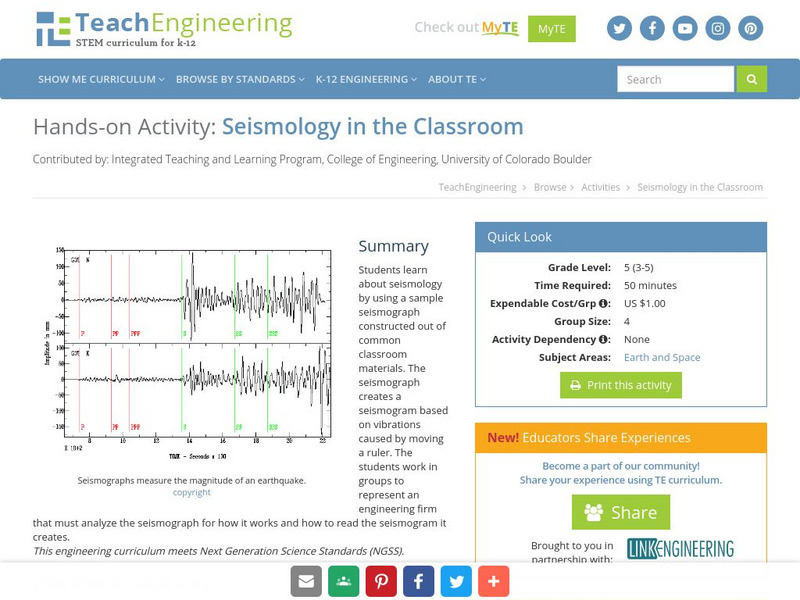
Students learn about seismology by using a sample seismograph constructed out of common classroom materials. The seismograph creates a seismogram based on vibrations caused by moving a ruler. The students work in groups to represent an...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Ready to Erupt!
Students observe an in-classroom visual representation of a volcanic eruption. The water-powered volcano demonstration is made in advance, using sand, hoses and a waterballoon, representing the main components of all volcanoes. During...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Mini Landslide
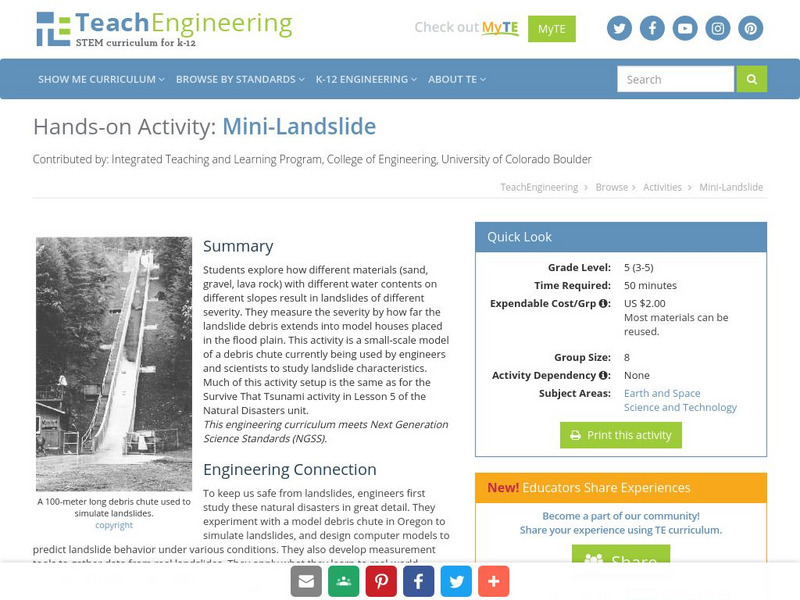
Students explore how different materials (sand, gravel, lava rock) with different water contents on different slopes result in landslides of different severity. They measure the severity by how far the landslide debris extends into model...
TeachEngineering
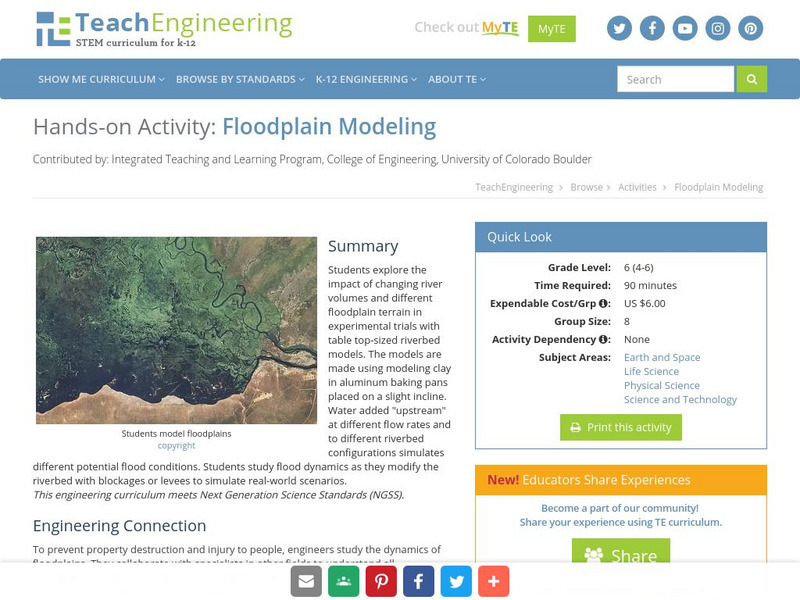
Teach Engineering: Floodplain Modeling
Students explore the impact of changing river volumes and different floodplain terrain in experimental trials with table top-sized riverbed models. The models are made using modeling clay in aluminum baking pans placed on a slight...
TeachEngineering
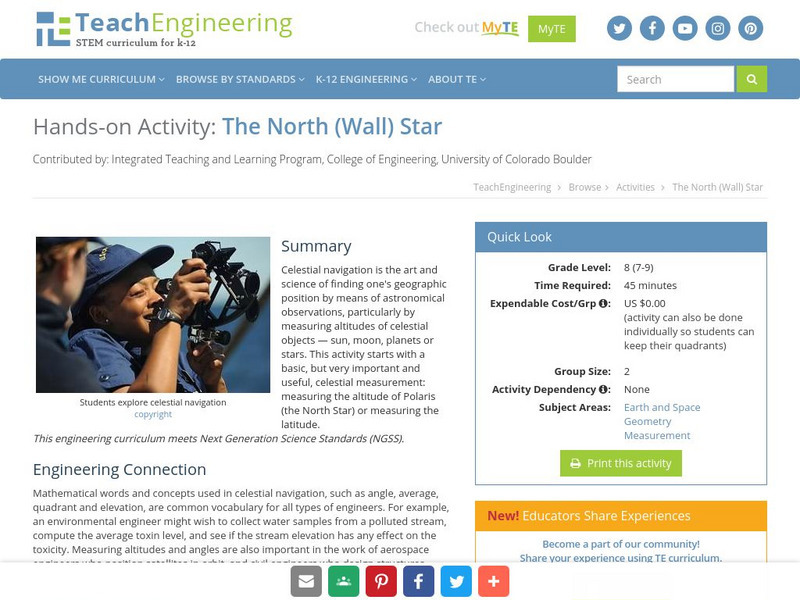
Teach Engineering: The North (Wall) Star
Celestial navigation is the art and science of finding one's geographic position by means of astronomical observations, particularly by measuring altitudes of celestial objects - sun, moon, planets or stars. This activity starts with a...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Stay in Shape
In this activity, students will learn that math is important in navigation and engineering. Ancient land and sea navigators started with the most basic of navigation equations (Speed x Time = Distance). Today, navigational satellites use...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Trig River
Students learn about and use a right triangle to determine the width of a "pretend" river. Working in teams, they estimate of the width of the river, measure it and compare their results with classmates.
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Close Enough?
Accuracy of measurement in navigation depends very much on the situation. If a sailor's target is an island 200 km wide, sailing off center by 10 or 20 km is not a major problem. But, if the island were only 1 km wide, it would be missed...
TeachEngineering
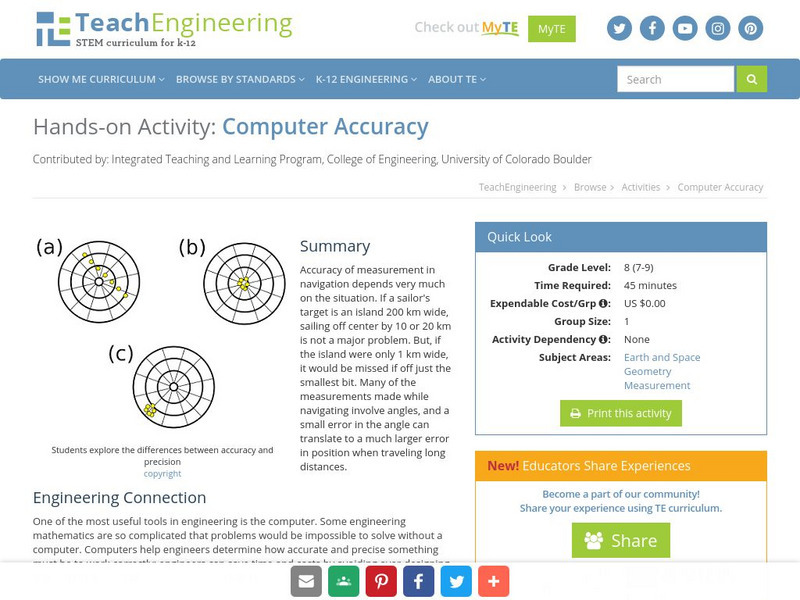
Teach Engineering: Computer Accuracy
Accuracy of measurement in navigation depends very much on the situation. If a sailor's target is an island 200 km wide, sailing off center by 10 or 20 km is not a major problem. But, if the island were only 1 km wide, it would be missed...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Classroom Triangles
In this activity, students will use bearing measurements to triangulate and determine objects' locations. Working in teams of two or three, students must put on their investigative hats as they take bearing measurements to specified...
TeachEngineering
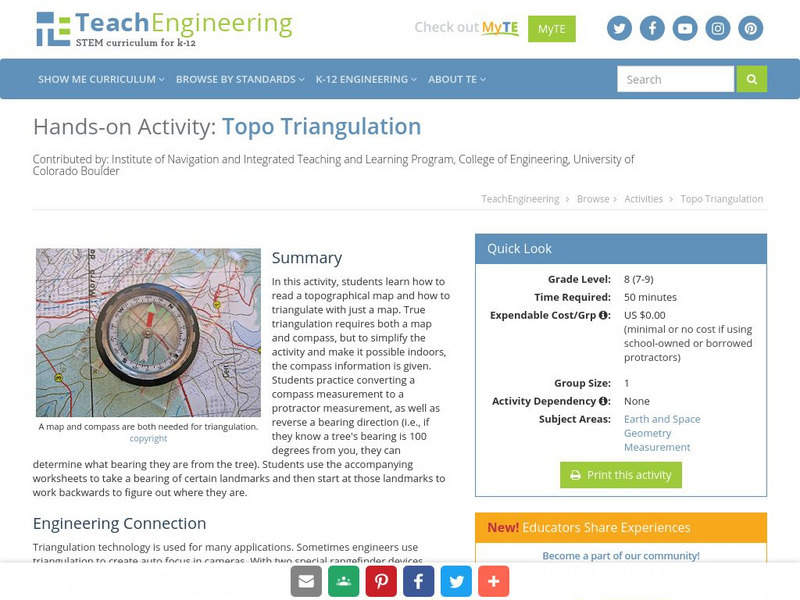
Teach Engineering: Topo Triangulation
In this activity, students will learn how to read a topographical map and how to triangulate with just a map. True triangulation requires both a map and compass, but to simplify the activity and make it possible indoors, the compass...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: State Your Position
To navigate, you must know roughly where you stand relative to your designation, so you can head in the right direction. In locations where landmarks are not available to help navigate (in deserts, on seas), objects in the sky are the...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Obi Wan Adobe: Engineering for Strength
Students conduct an experiment to determine how varying the composition of a construction material affects its strength. They make several adobe bricks with differing percentages of sand, soil, fibrous material and water. They test the...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Swinging With Style
Students experientially learn about the characteristics of a simple physics phenomenon - the pendulum - by riding on playground swings. They use pendulum terms and a timer to experiment with swing variables. They extend their knowledge...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Pump It!
Pumps are used to get drinking water to our houses every day! And in disaster situations, pumps are essential to keep flood water out. In this hands-on activity, student groups design, build, test and improve devices to pump water as if...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: A New Angle on Pv Efficiency
Students examine how the orientation of a photovoltaic (PV) panel relative to the sun affects the efficiency of the panel. Using sunshine (or a lamp) and a small PV panel connected to a digital multimeter, students vary the angle of the...
TeachEngineering
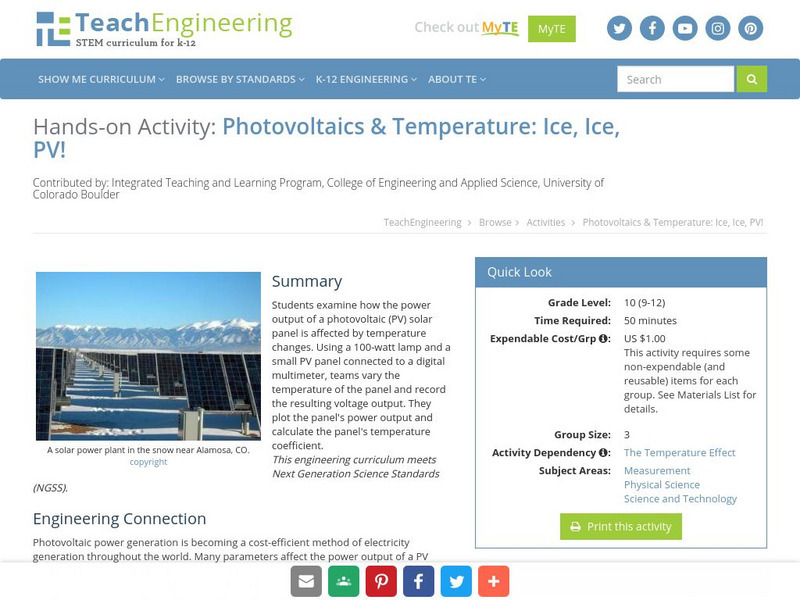
Teach Engineering: Ice, Ice, Pv!
Students examine how the power output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel is affected by temperature changes. Using a 100-watt lamp and a small PV panel connected to a digital multimeter, teams vary the temperature of the panel and record...
TeachEngineering
Teach Engineering: Pointing at Maximum Power for Pv
Student teams measure voltage and current in order to determine the power output of a photovoltaic (PV) panel. They vary the resistance in a simple circuit connected to the panel to demonstrate the effects on voltage, current, and power...