Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics
An incredible site! This is an interactive textbook that clearly and concisely covers any topic you can think of under both microeconomics and macroeconomics. Select "Table of Contents" to begin.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Saint Joseph's College: A Case of Inflation
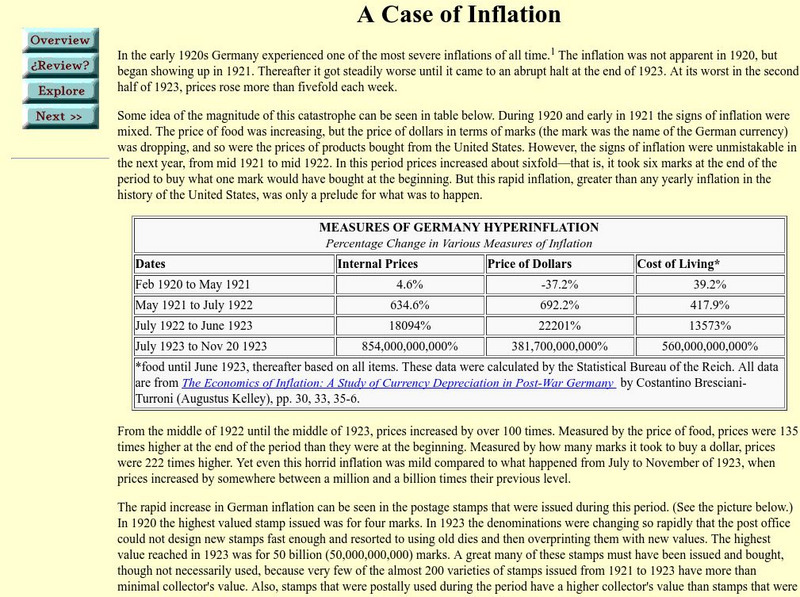
This overview of the hyperinflation in Germany following World War I describes not only its causes but what daily life was like for Germans whose money had become virtually worthless.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Measuring Income Distribution
E learning text offers information on measuring income distribution with the Lorenz Curve. Site presents charts and data for one to use in order to construct or analyze a Lorenz Curve.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Comparative Advantage
Article with charts and links to related material discusses how free trade is a result of comparative advantage, and how consumers can consume beyond their original production possibilities frontier if they specialize and trade.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Monopolistic Competition
E-learning site uses an example of "pushcarts on the beach" to demonstrate a monopolistically competitive market structure and how, as more firms enter the market, price, quantity, and deadweight loss are all affected.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Supply and Demand Overview
This is a site from the St. Joseph's College with an overview of the supply and demand model. It is actually the first page of a lesson on supply and demand complete with links to more in-depth discussions including graphs and charts...
Robert Schenk, PhD
Saint Joseph's College: Supply and Demand Buyer Equilibrium
Summarizes buyer equilibrium. Then click Next button at the bottom to learn about seller equilibrium as well as shortages & surpluses.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Measuring the Economy Inflation
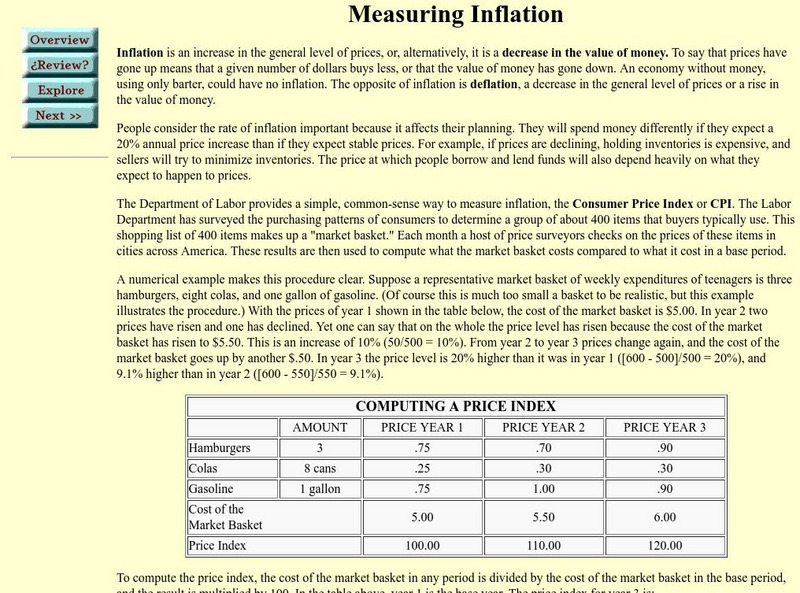
This site from the St. Joseph's College provides an explanation of inflation, including a section on how to calculate a consumer price index.
Robert Schenk, PhD
St. Joseph's College: Central Planning
This site examines the Soviet economic system during its Marxist period as an example of a planned economy.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Scarcity and Choice
This site from the St. Joseph's College examines the importance of scarcity and choice in terms of an economic system. A further explanation explores how various people have constructed utopias to assume away the problem of scarcity.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Monopolistic Competition
An example problem is given that shows how monopolistic competition works. Also an explanation of the model of monopolistic competition is given.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Gross Domestic Product
Provides a very thorough explanation of gross domestic product including charts and the calculation process.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Money Matters: The Gold Standard
This site provides a great article that explains the gold standard and why it didn't work for the United States and many other nations.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Rules of the Game Gold Standard & Macroeconomic Policy
A basic description of the struggles with the gold standard of the late 19th century in the United States, and William Jennings Bryan's attempts to abandon this.
Robert Schenk, PhD
More About Demand
This essay provides a good description of normal goods, inferior goods, substitutes, and complements, and how these are each related to the law of demand.
Robert Schenk, PhD
The Demand Curve
This site discusses demand and the law of demand, and shows how a demand schedule can be transferred onto a demand curve. It also explains how a change in the price of a substitute can cause your original demand curve to shift.
Robert Schenk, PhD
The Supply Curve
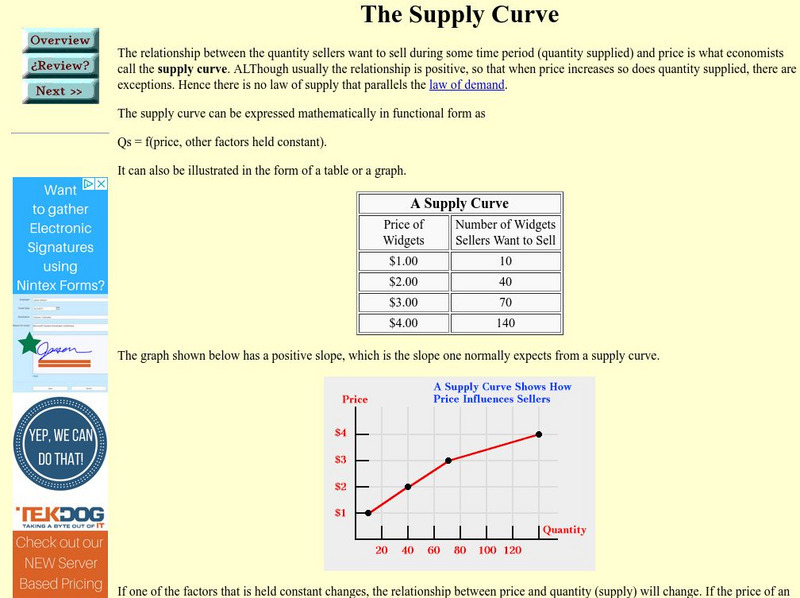
This site discusses supply schedules and supply curves, along with an example of how a supply curve may shift.
Robert Schenk, PhD
The Model of Supply and Demand
This site shows a supply and demand schedule, and constructs a graph using this schedule. It continues on to discuss equilibrium, and then shows a new equilibrium after there has been a change in supply.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Price Elasticity
This site offers a good description of price elasticity of demand for a good, and gives examples of which kinds of goods may be elastic or inelastic.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Computing Price Elasticity
This site discusses price elasticity, along with the formula for "arc elasticity," which is a different method to calculate price elasticity.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: Marginal Productivity and Income
Site provides a good description of the concept of "marginal productivity" along with other related terms such as marginal costs, marginal revenue product, and derived demand.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Saint Joseph's College: Shortages and Surpluses
This site provides easy to understand examples of shortages and surpluses, and what each looks like on a supply and demand graph.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: The Demand Curve for Output
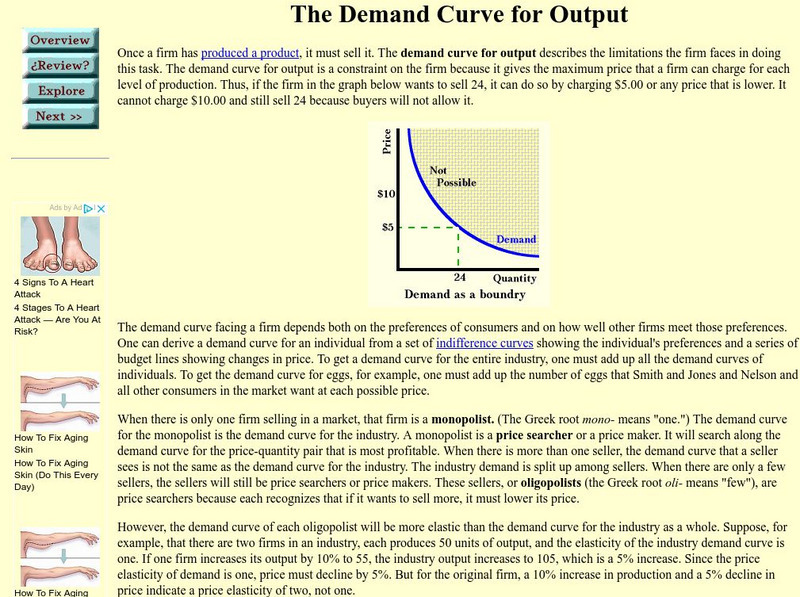
This site examines the relationship between a price taker and a price maker, and the market structure to which each might belong.
Robert Schenk, PhD
Cyber Economics: The Theory of Few Sellers
An overview of monopoly, oligopoly and duopoly, focusing on the interdependence of firms in an oligopoly, shown through the use of a game tree how these firms are tempted towards the practice of collusion.