Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Equations of Lines
In this task, 8th graders are presented with two intersecting line graphs and their linear equations. No values are shown on the axes. They are asked to interpret the constants in the equations in terms of their graphs, and make some...
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Who Has the Best Job?
This problem asks students to compare the incomes for two different jobs, draw their graphs, and explain whether the graphs alone would show who makes the most per hour. Aligns with 8.EE.B.5.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Orders of Magnitude
This problem discusses what is meant by an order-of-magnitude estimate and then asks students to make order-of-magnitude estimates for four different scenarios. Aligns with 8.EE.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Kimi and Jordan
This task looks at the job earnings plus weekly allowances of two people, all of which is saved. Students are asked complete tables showing their savings, write equations, draw their graphs, and compare the amounts they save each week....
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Coupon Versus Discount
For this task, 8th graders are asked to find at what price the cost of a calculator will be the same whether applying the store discount or using a coupon. Aligns with 8.EE.C.7.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Comparing Speeds in Graphs and Equations
This task provides the opportunity for students to reason about graphs, slopes, and rates without having a scale on the axes or an equation to represent the graphs. Aligns with 8.EE.B.5.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee the Sign of Solutions
Eighth graders are presented with five linear equations with one variable and are asked to state whether they have a positive solution, a negative solution, a zero solution, or no solution. Aligns with 8.EE.C.7.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Peaches and Plums
In this task, 8th graders are shown graphs of two linear functions and are asked to compare the costs per pound of two fruits without knowing their actual prices. To do this, they need to think about slope and unit rates. Aligns with...
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 8.ee Ants Versus Humans
This task requires students to work with large and small values expressed in scientific notation and in decimal notation, as well as to convert units of mass. Aligns with 8.EE.A.4 and 8.EE.A.1.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 5.nbt Are These Equivalent to 9.52?
Presents six sets of numbers in various formats and students are asked to determine which ones are equivalent to the decimal number 9.52 and to explain their reasoning. Aligns with 5.NBT.A and 5.NBT.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 5.nbt Elmer's Multiplication Error
Fifth graders are presented with the calculations for a multiplication problem and are asked to explain why the answer is incorrect. They must use estimation, identify the error, show the correct arithmetic, and find the answer another...
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 5.nbt Placing Thousandths on the Number Line
This task asks students to order decimal numbers to the thousandths on a number line between 0 and 0.1. Aligns with 5.NBT.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
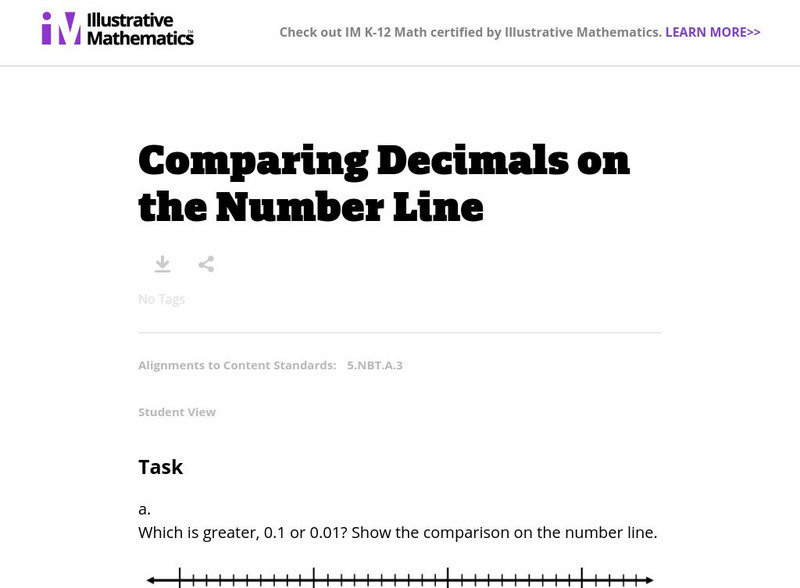
Illustrative Mathematics: 5.nbt Comparing Decimals on the Number Line
This task presents four pairs of decimal numbers and asks students to compare them and place them on number lines. Aligns with 5.NBT.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 5.md,oa You Can Multiply Three Numbers in Any Order
The purpose of this task is for students to use the volume of a rectangular prism to see why you can multiply three numbers in any order you want and still get the same result. Aligns with 5.OA.A and 5.MD.C.5.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.rp Converting Square Units
In this task, 6th graders must inches to feet in order to find the area of a rectangular board and explain the error in the calculations made by the board owner. Aligns with 6.RP.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.g Banana Bread
In this task about banana bread, 6th graders must calculate the volume of a pan to see if it is large enough for the bread batter. Aligns with 6.G.A.2.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.g Finding Areas of Polygons
This task presents drawings of polygons on square grids and asks students to calculate their area. They will need to use a few strategies, including decomposing and recombining shapes. Aligns with 6.G.A.1.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.g Christo's Building
This problem looks at a scale model of a project by Christo and Jeanne Claude. Students are asked to calculate its volume, how many 1/2-inch blocks would be needed to build it, and how much cloth would be required to wrap it. They then...
Illustrative Mathematics
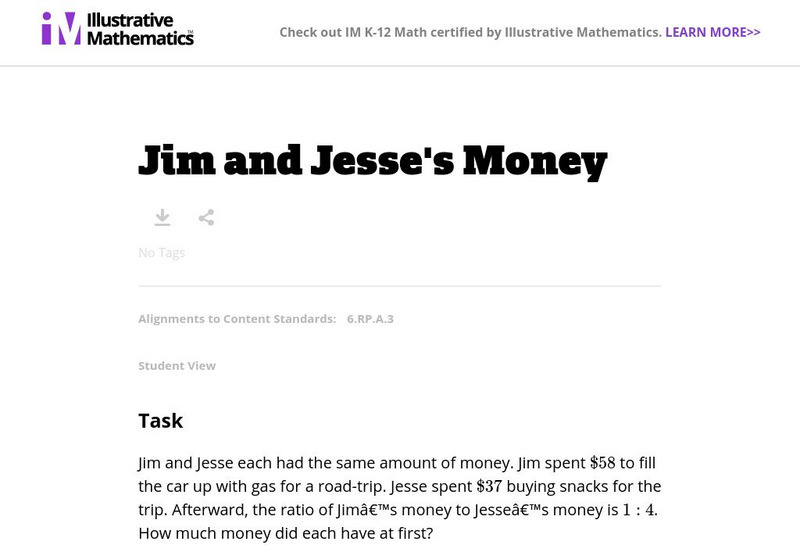
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.rp Jim and Jesse's Money
In this real-world context, 6th graders are given the ratio of Jim's money to Jesse's and the amounts they have spent so far on a road trip, and they must calculate what each person had at the start of the trip. Aligns with 6.RP.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
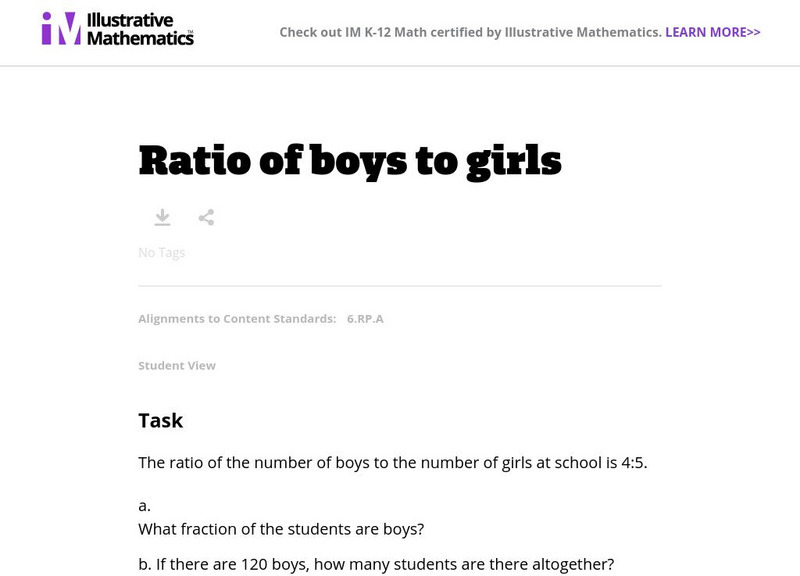
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.rp Ratio of Boys to Girls
Sixth graders work with a ratio stating the number of boys to girls in a school and use it to calculate the fraction of students who are boys and the total number of students. Aligns with 6.RP.A.
Illustrative Mathematics
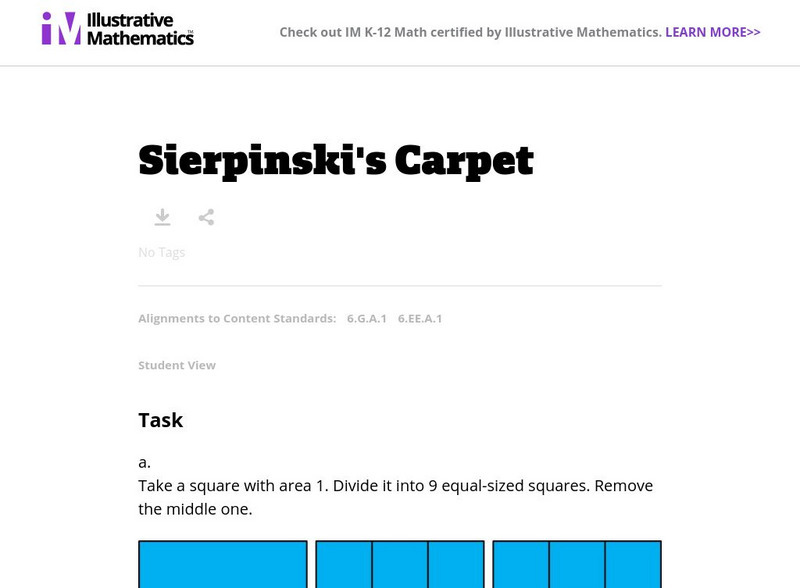
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.ee,g Sierpinski's Carpet
In this task, 6th graders are presented with a large square divided into 9 squares and the center square is then removed. They are asked to find the area of the 8 remaining squares. Each smaller square is divided in the same way and the...
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.g Painting a Barn
This task asks students to determine the area of the exterior walls of a barn and to calculate how many gallons of paint would be needed to cover them, as well as the cost of the paint. Aligns with 6.G.A and 6.RP.A.3.
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.g Computing Volume Progression 4
The purpose of this fourth task in a series of four is to find the volume of an irregular 3D solid by using Archimedes' Principle. Students must calculate the volume of the displaced water in a rectangular prism tank in order to solve...
Illustrative Mathematics
Illustrative Mathematics: 6.g Computing Volume Progression 3
The purpose of this third task in a series of four is to find the height of water in a rectangular prism tank when the volume is known. All units are metric. Aligns with 6.G.A.2.